Looking for the right and simplest way for MongoDB log rotation? Here’s how we do it.
A log file grows endlessly if we are not managing them properly and this cause many problems. An efficient solution to these problems with log file growth is log rotation.
At Bobcares, we often get requests on MongoDB log rotation, as a part of our Server Management Services.
In this write-up, we’ll do an analysis on MongoDB log rotation and see how our Support Engineers do this.
Why Log rotation ?
In MongoDB, the logs are not rotated automatically, so we rotate the logs manually.
Scheduling log rotation avoid problems like log file size growing larger, disk space issues, etc proactively. Today, we will discuss in detail on rotating logs in MongoDB.
MongoDB uses the logRotate rename behavior by default. With this, mongod or mongos renames the current log file by appending a UTC timestamp to the filename, opens a new log file, closes the old log file, and sends all new log entries to the newly created log file.
How we do MongoDB log rotation
Recently, one of our customers approached us saying that he is facing disk space issues due to large sized log files.
He asked us to suggest a solution as he couldn’t delete these logs permanently as he need them for future reference. So we suggested him log rotation. For that, we did the following:
Firstly, we start a mongod instance as the customer is using MongoDB.
mongod -v --logpath /var/log/mongodb/Servername.logCopy Code
Then we listed the log files and verified that the result contains servername.log.
Next, we rotated the log file by issuing the command from the admin database in mongo shell as shown below:
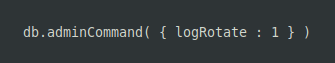
Then we confirmed whether the result contain two logs servername.log which is created when it reopened the log file and servername.log.<timestamp>, the renamed original log file.
We handled many queries and in another case we followed logRotate reopen method.
Firstly, we started a mongod instance, specifying reopen –logRotate behavior.
mongod -v --logpath /var/log/mongodb/servername.log --logRotate reopen --logappendCopy Code
Then we confirmed that servername.log is included in the result and rotated the log using the command ‘db.adminCommand( { logRotate : 1 } )’ from admin database in mongo shell. Also, we renamed the file using some external process.
We successfully rotated the logs in both the cases.
[Need any further assistance with MongoDB? – We can help you]
Conclusion
In conclusion, MongoDB log rotation can be done in different ways manually, and we saw how our Support Engineers do this for our customers.




0 Comments