Due to its ‘light-weight’ reputation, container technologies such as Docker and LXC get a lot of attention from online businesses these days.
Docker and LXC are suited for different purposes. But in the flurry of information floating in the internet, these differences often get overlooked.
Stabilize your virtualization system
Today we’ll discuss the major differences between Docker and LXC, and where to use them.
1. Full system virtualization Vs App virtualization
Containers can be broadly classified into two, based on the depth of virtualization they provide : Containers such as LXC, that enable full system virtualization and those like Docker, that give application virtualization.
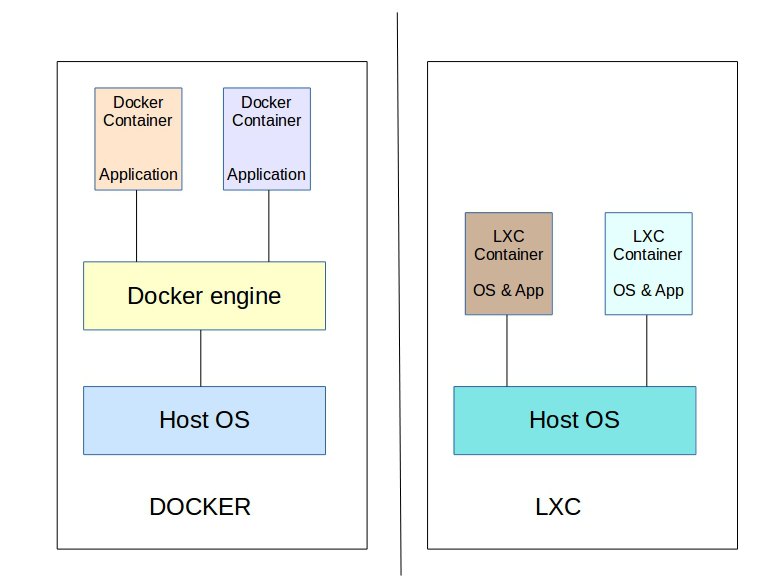
LXC vs Docker – Architecture comparison
In full system virtualization, users would get their preferred OS flavor and can install their required applications such as web, mail, etc. in the container. That makes LXC containers similar to VMs.
Application virtualization is focused on a single application. A Docker container, when started, runs a single process, which is the application for which it is intended.
In short, LXC containers can execute multiple applications and processes, while Docker containers are restricted to a single application or a service.
So LXC containers can be used to host virtual environments for private hosting, just like how VMs are used. But for application development and testing requirements where quick deployments are needed, Docker containers are suited.
[ Are your spending too much time managing your virtualization system? Our server management experts take care of your infrastructure and ensure its smooth functioning. ]
2. Data persistence
LXC containers are complete virtualization entities with its own file system. So any data updated in an LXC container, will always be retrievable.
In a Docker container, on the other hand, changes made to the data cannot persist beyond a restart. (However, note that, with the help of Docker volumes, it is possible to retain the data changes in the host).
As a result, Docker containers are often considered ‘stateless’ and cannot be edited once deployed. LXC, on the other hand, is stateful and stores data.
So, if you want a single container solution to manage data belonging to multiple applications and services, LXC is the ideal choice over Docker.
But if you need application deployments with
Read: How to setup high density VPS hosting using LXC
3. Single purpose Vs Multi-purpose
LXC containers are multi-purpose as they allow multiple applications to execute in them. Docker containers, on the other hand, are single purpose containers that host only one application or service.
For small and medium businesses which require multiple applications and services such as WordPress, Email, MySQL, Apache, etc., LXC containers are apt.
Designing a Docker system to support multiple applications require complex setup and coding, which is a waste of time, whereas LXC readily provides that feature.
Docker containers are suitable for developers who want to develop and ship immutable images of their applications across different platforms for use.
Hosting services using Docker containers is suitable when you want one server to run independent of the other. For instance, you can shut down the MySQL container without interrupting the Apache container.
But, by default, the Docker containers are not externally accessible and you need to make them accessible by exposing their ports, inorder to host services in them.

Docker containers with single application
Read: Building a WordPress virtualization solution using LXD/LXC containers
4. Platform independence
LXC, as the name suggests, are Linux containers and cannot be ported easily to run on other OS. On the other hand, Docker containers can run on any system that support Docker Engine.
As Docker Engine is supported on almost all OS such as Linux, Windows and MacOS, Docker containers running an application can be ported easily to any of these platforms.
Thus, while Docker is suited for deploying and testing applications in different OS versions, LXC containers are suited for setting up a complete set of business services in Linux OS.
[ Running a virtualization infrastructure doesn’t have to be hard, or costly. Get world class server management services at affordable pricing. ]
5. Security and isolation
A popular way by which malware spreads is via cross-site contamination. In LXC, there are multiple applications running in the same environment.
A malware uploaded via one compromised application can possibly spread to other applications or cause downtime to other services. But it is possible to secure the LXC containers using AppArmor or SELinux.
In contrast, Docker has each application running in its own isolated environment. Using SELinux and namespaces, a Docker instance can be fully secured to prevent any cross-site contamination.

LXC architecture
In short..
Container virtualization is ideal for users who prefer light-weight and easily-manageable instances. Here we’ve broadly covered the scope of Docker and LXC containers.
Choosing the technology that suits each business purpose, securing each instance, customizing the OS images and managing the deployments, etc. are also critical aspects to be taken care of.
If you’d like to get more assistance regarding choosing the best infrastructure for your business or want to make your server infrastructure more efficient, we’d be happy to talk to you.








0 Comments