Learn how to fix the Fatal error: Cannot instantiate interface in Magento 2. Our Magento Support team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
Fixing Magento 2 ‘Cannot Instantiate Interface’ Errors
Did you run into an error while trying to run a CLI command in Magento after an upgrade?
Fear not! Our experts are here to help you out. The error message typically looks like this:
Cannot instantiate interface Klevu\Search\Api\Service\Catalog\Product\StockServiceInterface#0 /var/www/html/vendor/magento/framework/ObjectManager/ObjectManager.php(70): Magento\Framework\ObjectManager\Factory\Dynamic\Developer->create(‘Klevu\\Search\\Ap…’)
#1 /var/www/html/vendor/klevu/module-productsearch/Helper/Stock.php(29): Magento\Framework\ObjectManager\ObjectManager->get(‘Klevu\\Search\\Ap…’)
- How to Fix the Post-Upgrade Issue
- Common Causes of the Error
- Troubleshooting Tips
How to Fix the Post-Upgrade Issue
To resolve this issue and successfully run Magento commands, we need to flush all Redis sessions.
- Flush the Redis Cache:
Run the command to flush the Redis cache.
warden redis flushallThis will result in ‘OK’ as the output.
- Run Magento Commands:
After the Redis cache is flushed, we can run any Magento command, such as:
php bin/magento cache:flush
php bin/magento setup:upgrade
php bin/magento setup:di:compile
Common Causes of the Error
- The `di.xml` file may lack the necessary mapping between the interface and its concrete implementation.
- The `di.xml` file may have incorrect mappings, causing Magento to attempt to instantiate an interface directly.
- Furthermore, outdated or corrupted code generation can lead to dependency resolution failures in Magento.
Troubleshooting Tips
- Enabling debug mode offers more detailed error messages in the Magento logs. This will help find the problematic configuration.
- Verify that the `di.xml` file correctly maps interfaces to their implementations. This file is located in the `etc` directory of a module.
For example:
If we have an interface `Vendor\Module\Api\MyInterface` and a class `Vendor\Module\Model\MyClass` implementing this interface, configure the DI container to map the interface to the implementation.
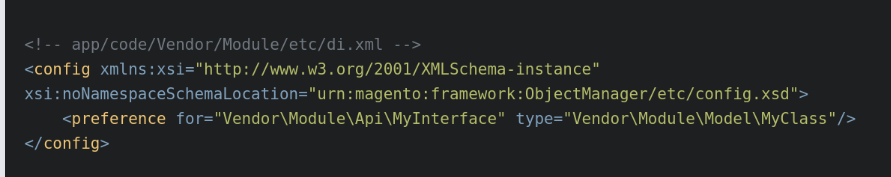
- Also, make sure the class constructors correctly declare their dependencies.
For example:
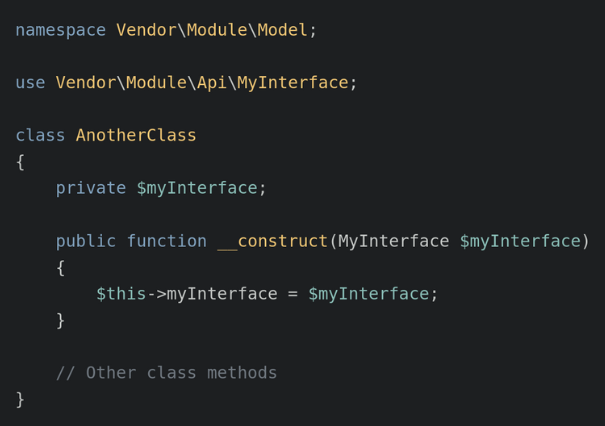
- Next, clear and regenerate Magento’s generated code.
php bin/magento setup:di:compile
php bin/magento cache:clean
php bin/magento cache:flush - We need to make sure no conflicting modules override or interfere with the dependency injection configurations.
- Also, look for conflicting preferences in `di.xml` files across different modules.
- Furthermore, make sure there are no duplicate or conflicting class definitions.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to fix the Fatal error: Cannot instantiate interface in Magento 2







0 Comments