Docker performance can be affected by a single container that abuses the CPU or memory, which can eventually end up crashing other containers or the entire machine.
Most hosting providers implement QoS (Quality of Service) to improve Docker performance. This includes limiting resources per container and monitoring their usage.
How resource usage impacts Docker performance
The main resources that are shared among containers in a Docker host includes memory, CPU and block I/O.
The resource usage of a container can be seen with the command ‘docker stats container-ID‘. It will list the CPU, memory and I/O usage for that container.
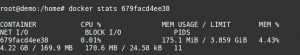
Docker container stats
During less traffic hours, the resources allotted for the containers would be sufficient to manage the load in them and the Docker performance would be fine.
But when traffic peaks or one Docker container suddenly start abusing the resources in the host, the Docker performance would start getting affected.
To improve performance, its vital to limit the resources per container for QoS (Quality of Service). This can be achieved using the ‘cgroups’ (control groups) feature.
Speed up your Docker containers
Today, we’ll discuss how to improve Docker performance by limiting the memory and CPU usage in containers using cgroups.
How to improve CPU performance for Docker containers
CPU usage plays a vital role in determining the Docker performance. The CPU share that is allotted to all containers by default is 1024.
If all the containers have this default value set, the available CPU will be shared among them equally. Without CPU limits, one container can use up all the available CPU.
Suppose you need to allot more CPU share to a container or limit the CPU for one container, based on their plans. This can be achieved by setting CPU weights.
In a machine with 3 containers, if one is assigned 1024 CPU share and others are assigned 512 CPU share, then first one will get 50% CPU and others 25% each.
The CPU shares would be divided among the containers based on the total number of containers and the CPU share value assigned to each.
To assign a CPU share to a container during creation or run-time, the ‘-c’ flag can be used with ‘docker run’ command. Here, a CPU share of 512 is assigned:
Assign CPU shares for Docker container
In multi-core machines, the CPU share has to be calculated by considering the number of CPUs also, along with the container count and usage plans.
It is also possible to allocate the CPU usage of a container to a certain CPU core, in a multi-core machine. Many more tweaking can be done based on the requirements.
The cgroups CPU metrics and stats are stored in the files inside the folder ‘/sys/fs/cgroup/cpuacct/docker/container-ID/’ as seen:
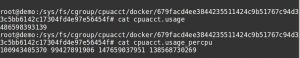
Docker container CPU stats
[ Are your spending too much time managing your Docker containers? Our Docker experts take care of your infrastructure and ensure its smooth functioning. ]
How to set memory QoS for containers using Docker cgroups
Similar to CPU, the memory limit of containers also plays a crucial role in Docker performance. Memory limits can be set with cgroups, using its memory subsystem.
The default setting is no memory limit, which means that the container can use as much free memory in the host machine as possible.
This is a dangerous setting as one abusive script can crash the entire machine. To set a container’s memory usage to a fixed limit, the flag ‘-m’ is used in ‘docker run’ command.
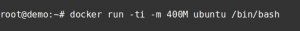
Assign memory limits for Docker container
In this instance, the container can use 400M memory and 400M swap memory. The swap memory limit can be set to a separate value, if required.
So the container will be limited to 800M total memory usage and will not be able to hog more memory from the host machine.
The docker cgroups memory metrics and stats are stored in the files inside the folder ‘/sys/fs/cgroup/memory/docker/container-ID/’ as seen:
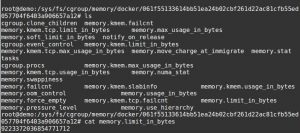
Docker container memory stats
[ Running a Docker infrastructure doesn’t have to be hard, or costly. Get world class Docker management services at affordable pricing. ]
How to achieve block I/O performance for Docker containers
Block I/O (Blkio) bandwidth assigned to the containers is another resource that needs to be limited for Docker performance.
The default setting is to allot equal share of Blkio among the containers, the value being 500. This can be changed using the ‘–blkio-weight’ flag in ‘docker run’.
Assign block I/O limit for Docker containers
Weight that can be set to the ‘–blkio-weight’ flag can be a value between 10 and 1000, depending on the container requirements.
The docker cgroups Blkio metrics and stats are stored in the files inside the folder ‘/sys/fs/cgroup/blkio/docker/container-ID/’.
Docker I/O stats for containers
To summarize..
Resource control and constant performance monitoring is crucial for smooth running of a Docker infrastructure.
In this post, we discussed how we improved Docker performance by implementing resource control for QoS using cgroups, in the containers.
Bobcares helps Docker systems deliver high performance through our expert resource management, control and monitoring services.
If you’d like to know how to manage your Docker infrastructure resources to get the best out of them for your business, we’d be happy to talk to you.








0 Comments