The GSUTIL Wildcard rm delete objects with gsutils following a wildcard pattern. As part of our Google Cloud Platform Support Service, Bobcares provides answers to all of your questions.
GsUTIL Wildcard RM
Removing an object cannot be undone. However, with Google Cloud Storage, developers have remarkable flexibility and control over their data. Also, Google strictly regulates how deleted data is handled and removed. On the bucket(s), we can set up object versioning to safeguard ourself against errors. The gsutil rm command removes objects. Let’s look into the details:
1. The code
gsutil rm gs://bucket/subdir/*2. The code
gsutil rm gs://bucket/subdir/**3. The following commands can remove gs://bucket/subdir and all objects and subdirectories under it:
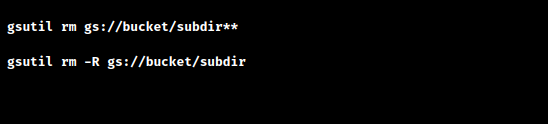
For versioning-enabled buckets, the ** command will only remove the live version of each item in the subdirectory; in contrast, the -R option will also remove all object versions in the subdirectory.
4. Running gsutil rm -R on a bucket
gsutil rm -R gs://bucket5. We can use code
gsutil rm gs://bucket/**6. Use the gsutil -m option to execute a parallel (multi-threaded/multi-processing) remove if we have a lot of objects to get rid of:
gsutil -m rm -R gs://my_bucket/subdir7. Commands like
gsutil rm *.txt8. In order to delete objects with gsutils following a wildcard pattern, we can try
gsutil rm -r gs://bucket/folder/{WILDCARD-A}/folderA/{WILDCARD-B}/folderBWe can use the gsutil -m option to allow multi-threading/multi-processing if we have a lot of objects to remove. Avoid using gsutil if we need to mass delete 100,000 or more objects because it takes a long time to finish. Alternatively, we can use Object Lifecycle Management, which can delete any number of objects, or the Google Cloud console, which can delete up to several million things.
9. When using wildcards in gsutil to delete a specific subdirectory, we must enclose the wildcards in single or double quotes.Before gsutil notices it (and complains that no local files match the wildcard), zsh is trying to enlarge the wildcard. Kindly attempt the following to stop zsh from doing so:
gsutil rm 'gs://bucket/**'[Want to learn more? Click here to reach us.]
Conclusion
To conclude, the article offers the a detailed explanation on use of GSUTIL RM command in Wildcards.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.







0 Comments