Learn more about the unauthenticated RCE Flaw With CVSS 9.9. Our Server Management Support team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
Unauthenticated RCE Flaw With CVSS 9.9
Recently, the security community has been alerted to several critical vulnerabilities in CUPS (Common UNIX Printing System), affecting various Linux distributions.
According to our Experts, while Red Hat Enterprise Linux users are impacted, the default configurations are generally safe. These vulnerabilities, however, pose a moderate risk, with specific distributions still assessing their exposure levels.
Security researcher Simone Margaritelli identified four key vulnerabilities, which have been allocated the following CVEs:
- CVE-2024-47076
- CVE-2024-47175
- CVE-2024-47176
- CVE-2024-47177
Let’s take a closer look at what’s known so far.
An Overview:
- Key Dates for Vulnerability Disclosure
- A Closer Look at the CUPS Vulnerabilities
- Red Hat’s Insight on Mitigation
- Action Plan: Remediating the CUPS Vulnerabilities
- High Severity and Ease of Exploitation
- What Enterprises Should Do
- Navigating the Uncertainty: How to Stay Safe
Key Dates for Vulnerability Disclosure
Though detailed information about these vulnerabilities remains limited, the security community has established a timeline for full disclosure:
- September 30th: Initial disclosure to the Openwall security mailing list.
- October 6th: Full public disclosure of the vulnerability details.
A Closer Look at the CUPS Vulnerabilities
These vulnerabilities could lead to remote code execution (RCE), enabling attackers to take control of affected systems. Here’s a breakdown of the identified CVEs:
- CVE-2024-47176:
In versions of `cups-browsed` ≤ 2.0.1, it binds to `UDP INADDR_ANY:631`, allowing an attacker to trigger a Get-Printer-Attributes IPP request from any source to a malicious URL.
- CVE-2024-47076:
In `libcupsfilters` ≤ 2.1b1, the `cfGetPrinterAttributes5` function does not validate IPP attributes from a server, providing unchecked data to the rest of the CUPS system.
- CVE-2024-47175:
The `libppd` function `ppdCreatePPDFromIPP2` does not sanitize IPP attributes, potentially injecting malicious data into a temporary PPD file.
- CVE-2024-47177:
The `foomatic-rip` in `cups-filters` ≤ 2.0.1 allows arbitrary command execution through the `FoomaticRIPCommandLine` PPD parameter.
Red Hat’s Insight on Mitigation
Red Hat has provided guidance on how to mitigate these vulnerabilities, especially in environments where printing services are unnecessary. Here’s how an exploitation scenario could unfold:
- The `cups-browsed` service is manually enabled or started.
- An attacker gains access to a vulnerable server, either by:
- Exploiting unrestricted access (e.g., via the public internet), or
- Accessing an internal network where local connections are trusted.
- Then, the attacker advertises a malicious IPP server, provisioning a malicious printer.
- A victim attempts to print, triggering the attacker’s arbitrary code execution.
Action Plan: Remediating the CUPS Vulnerabilities
Mitigating these vulnerabilities is relatively straightforward. Here’s what we can do:
- Stop and remove the service if it’s not needed in the environment.
- Implement firewall rules to block traffic on UDP port 631 and, if applicable, restrict or disable mDNS/DNS-SD services.
- Apply security updates for CUPS and related components as soon as they become available.
Linux systems are widely used in enterprise servers, cloud environments, and critical applications. As a result, this vulnerability affects numerous servers, desktops, and even embedded devices around the world.
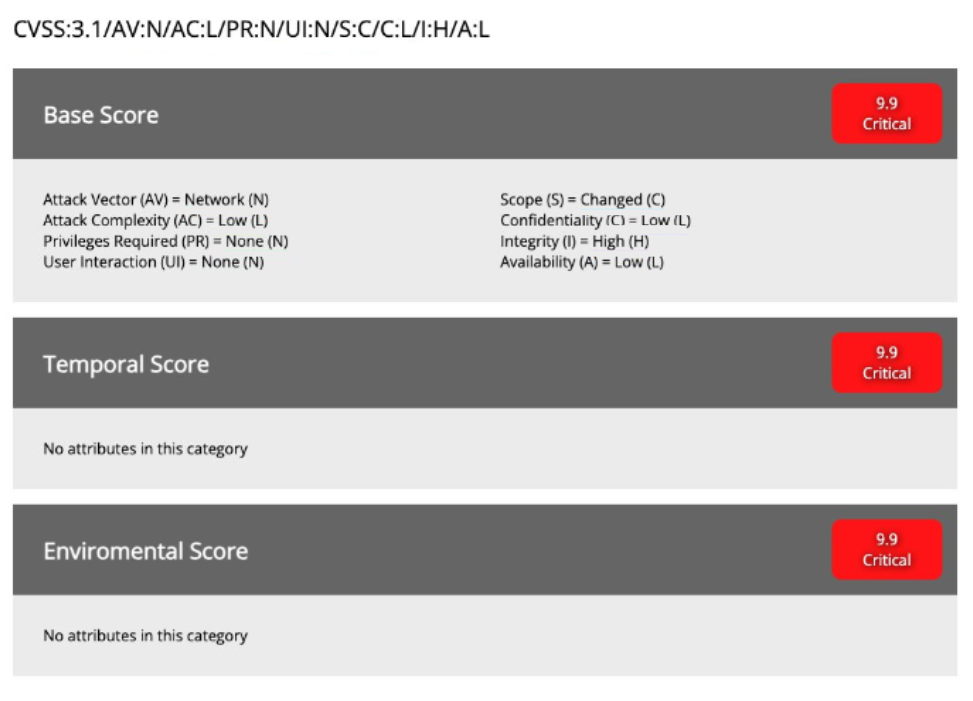
High Severity and Ease of Exploitation
The CVSS score for this vulnerability is 9.9, making it critical.
- Attackers don’t need valid credentials to exploit this vulnerability.
- Also, attackers can execute arbitrary code on affected systems, potentially gaining full control.
- Until a fix is released, systems remain vulnerable.
While this vulnerability primarily affects GNU/Linux systems, other platforms using CUPS, such as macOS and various Unix derivatives, could also be at risk.
What Enterprises Should Do
Enterprises should take proactive steps to minimize exposure:
- Evaluate the exposure risk for the CUPS systems.
- Restrict access to the printing system where possible.
- Furthermore, turn off services like `cups-browsed` if not needed.
- Be ready to patch as soon as updates are available, and test thoroughly to avoid service interruptions.
Navigating the Uncertainty: How to Stay Safe
Until full details and patches are available, the best course of action is to stay informed. Monitor official sources for updates and be prepared to act swiftly when the patch is released.
Here are the key takeaways:
- A critical CUPS vulnerability has been reported, with a CVSS score of 9.9.
- Full disclosure is expected by October 6th, 2024.
- Additionally, the vulnerabilities highlight the importance of maintaining secure and updated systems.
- Also, enterprises should assess their exposure, limit network access, and prepare for rapid patch deployment.
Stay tuned for more details as they become available, and ensure your systems remain secure during this period.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In brief, our Support Experts introduced us to the unauthenticated RCE Flaw With CVSS 9.9 and how it can affect us.







0 Comments