Are you using Nagios and unable to delete the host? We can help you with deleting it.
Here at Bobcares, we have seen several such Nagios-related errors as part of our Server Management Services for web hosts and online service providers.
Today we’ll take a look at the causes for this error and see the fix.
Why is Nagios unable to delete the host?
Generally, you can delete the host using Core Config Manager by selecting the Delete icon from the Host Management page. That is, Configure >> Core Config Manager >> Services (delete all host’s dependencies) >> Hosts >> Delete host
But sometimes, in Nagios XI when you try to delete or deactivate a host through the Core Configuration Manager, you may get the following error (or one similar to it) in a red box near the top of your screen:
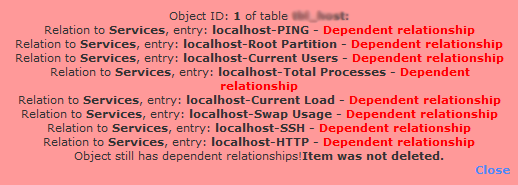
How we fix the problem when Nagios is unable to delete the host
Now let’s take a look at how our Support Engineers resolve this error for our customers.
- In order to delete or deactivate a host, we suggest our customers first delete or deactivate all of the services and other objects that are attached to it.
- Using services as an example, first, we click the Services link in the left-hand navigation pane of the Core Configuration Manager.
- Then, using the search bar we find the services that are attached to the host we wish to delete.
- Generally, these will be named after the host, so we search for the hostname.
- However, sometimes, they will not be named after the host if they were created manually or the name was modified. Then in such cases, we search them directly using their specific names as mentioned in the red error box.
- Once we’ve found the attached services we select which to delete or deactivate. To do it, we check their individual checkboxes. These checkboxes are located to the left of their entries in the search results table.
- Then we select or deselect all the displayed services. For that, we check or uncheck the box to the left of the words “Config Name” at the top of the table.
- After selecting the desired services, we use the “With Checked” dropdown box located beneath the search results table to choose the desired action.
- Finally, we choose the Delete option to remove the services from the Core Configuration Manager database. Whereas Deactivate will leave them but not apply them to the active configuration. This is useful if you may need to reactivate the services later.
Once we delete or deactivate the services, we go back to the host and delete or deactivate it as well if necessary.
[Need any further assistance in fixing Nagios errors? – We are here to help you]
Conclusion
Today, we saw the solution our Support Engineers provide to our customers when they are not able to delete the host in Nagios.




0 Comments