Learn how to deploy MySQL Statefulset with Helm Chart. Our MySQL Support team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
MySQL StatefulSet Helm Chart | How to Deploy
Deploying MySQL on Kubernetes requires special attention to data persistence and scalability. This is where MySQL Statefulset comes in handy. It ensures data consistency across pods and facilitates scaling operations seamlessly.

Today, we are going to take a look at the deployment process using Helm.
MySQL operates as a stateful application, storing important data within volumes. Without a Statefulset, data stored in pod ephemeral storage will vanish when the pod restarts.
Additionally, as demand surges, we have to scale MySQL to multiple pods. The Statefulset ensures data consistency across pods, such as mysql-0 and mysql-1, providing a stable foundation.
How to Installing the Chart
Let’s dive into the installation process using Helm to deploy MySQL on our Kubernetes cluster.
$ helm repo add bitnami https://charts.bitnami.com/bitnami
$ helm install my-release bitnami/mysql
These commands start the deployment, setting up MySQL with default configurations. Next, we explore how to tailor these configurations to our specific needs.
Customizing the Installation
To customize the installation, we can use the `–set` option with `helm install` or provide a YAML file specifying parameter values.
For instance:
$ helm install my-release \
--set auth.rootPassword=secretpassword,auth.database=app_database \
bitnami/mysql
This command sets the MySQL root password and creates a database named app_database.
Creating the Service
Now, create the service using the provided service.yml configuration file:
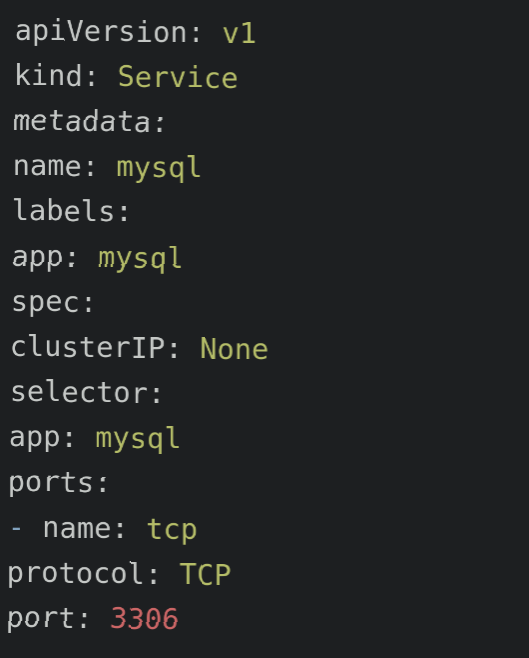
Apply the service:
$ kubectl apply -f service.ymlCreating the StatefulSet
Now, it is time to create the StatefulSet using the statefulset.yml configuration file:
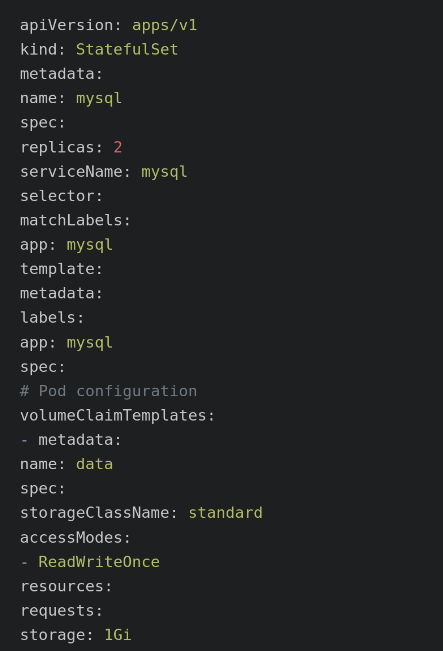
Apply the StatefulSet:
$ kubectl apply -f statefulset.ymlVerifying and Scaling
Check the deployment status with:
$ kubectl get sts
$ kubectl get pods -l app=mysql
Access the MySQL pod:
$ kubectl exec -it mysql-0 -- mysql -u root -pNow, we are connected to the MySQL database. We can create tables and data as needed.
To scale the replica set:
$ kubectl scale sts mysql --replicas 3Cleaning up
To tidy up resources, follow these steps:
$ kubectl delete pod mysql-client-loop --now
$ kubectl delete statefulset mysql
$ kubectl get pods -l app=mysql
$ kubectl delete configmap,service,pvc -l app=mysql
This setup ensures the MySQL deployment is resilient and can handle evolving workloads.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to deploy MySQL Statefulset with Helm Chart.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.







0 Comments