Learn how to send emails with xp_sendmail in SQL Server. Our SQL Server team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
Sending Emails with xp_sendmail in SQL Server
If you’re working with SQL Server and need to send emails directly from your database, you may have come across `xp_sendmail`.
This handy stored procedure lets us send emails using a MAPI client like Outlook.
Although newer versions of SQL Server offer the simpler `sp_send_dbmail`, `xp_sendmail` remains a valuable tool. It is useful when we need emails to be sent regardless of the transaction’s outcome.
`xp_sendmail` is a system procedure in SQL Server that sends messages to specified recipients. Also, this message can either be plain text or the result of a Transact-SQL query. Unlike `sp_send_dbmail`, which uses SMTP and doesn’t require additional software, `xp_sendmail` needs a MAPI client like Outlook installed on the server.
Syntax of xp_sendmail
Here’s the basic syntax for `xp_sendmail`:
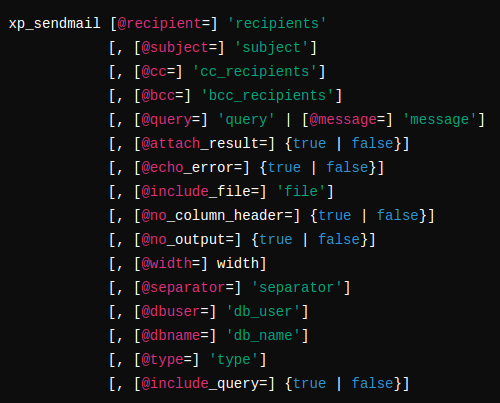
Here are the key parameters:
- recipient: Email address of the recipient(s). Separate multiple addresses with semicolons.
- subject: Optional email subject. Defaults to “Sybase SQL Server Message”.
- cc_recipient: List of CC recipients, separated by semicolons.
- bcc_recipient: List of BCC recipients, separated by semicolons.
- query: Transact-SQL query whose results are sent in the email.
- message: Text of the email message. Cannot be used with `query`.
- attach_result: If true, attaches the query result to the email; if false, includes the result in the email body. Default is false.
- echo_error: Includes error messages in the query results. Default is true.
- include_file: Files to attach to the email, separated by semicolons.
- no_column_header: If true, excludes column headers from query results. Default is false.
- no_output: If true, suppresses output to the initiating session. Default is false.
- width: Width of the result set in characters. Default is 80 characters.
- separator: Character used to separate columns in the query result. Default is the tab character.
- dbuser: Database user name for query execution. Default is “guest”.
- dbname: Database name for query execution. Default is “master”.
- type: Message type based on MAPI mail definition. Only “CMC:IPM” is supported.
- include_query: If true, appends the query to the result set. Default is false.
Here’s an example of using `xp_sendmail` to send an email with an attachment:
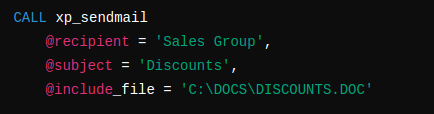
Furthermore, only system administrators have the necessary permissions to execute `xp_sendmail`. However, they can grant access to other users as needed.
While `xp_sendmail` requires a MAPI client and some setup, it remains a powerful tool for sending emails directly from SQL Server, especially when transactional independence is required. So, we can use `xp_sendmail` to boost the SQL Server’s email capabilities.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to send emails with xp_sendmail in SQL Server.




0 Comments