Let’s fix the “Ansible Error: Mapping Values Are Not Allowed in This Context.” As part of our DevOps Support Services, Bobcares provides answers to all of your questions.
Overview
- Resolving “Ansible Error: Mapping Values Are Not Allowed in This Context”
- Key Impacts
- Causes and Fixes
- Prevention Tips
- Conclusion
Resolving “Ansible Error: Mapping Values Are Not Allowed in This Context”
The “mapping values are not allowed in this context” error is a YAML syntax issue that occurs in Ansible playbooks. This error stops the playbook from running and disrupts configuration management processes. The Common Error Message is as follows:
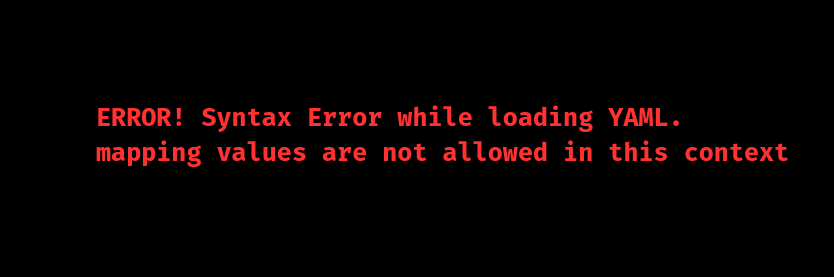
Key Impacts
1. Playbook Execution Failure: No tasks are executed, halting the deployment process.
2. Workflow Disruption: Automated scripts and system updates are interrupted.
3. Debugging Challenges: Locating syntax issues requires manual inspection.
4. Deployment Blockage: Continuous integration/continuous deployment (CI/CD) pipelines are disrupted.
Causes and Fixes
1. Incorrect Indentation
Cause: Misaligned YAML elements.
Fix: Use consistent spaces (no tabs) and proper indentation.
Example:
Incorrect:
tasks:
service:
name: apache2
Correct:
tasks:
– service:
name: apache2
2. Unescaped Special Characters
Cause: Special characters in values cause parsing errors.
Fix: Use quotes or escape characters.
Example:
Incorrect:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: https://$host/oauth2/auth
Correct:
annotations:
nginx.ingress.kubernetes.io/auth-url: “https://$host/oauth2/auth”
3. Improper Nesting of Mappings and Sequences
Cause: Incorrectly structured key-value pairs or lists.
Fix: Ensure proper nesting with correct indentation.
Example:
Incorrect:
– hosts: webservers
service:
name: apache2
state: started
Correct:
– hosts: webservers
tasks:
– service:
name: apache2
state: started
4. Missing Spaces After Colons
Cause: Missing space between a key and its value.
Fix: Always add a space after colons.
Example:
Incorrect:
key:value
Correct:
key: value
5. Mixing Tabs and Spaces
Cause: Using both tabs and spaces for indentation.
Fix: Use spaces consistently and configure your editor to convert tabs to spaces.
Prevention Tips
1. Use YAML Linters:
Tools like yamllint can automatically detect formatting errors.
2. Consistent Formatting:
Use 2 spaces for each level of hierarchy.
Avoid tabs entirely.
3. Validate Before Deployment:
Use online YAML validators.
Include YAML checks in CI/CD pipelines.
4. Editor Configuration:
Enable features to show whitespace.
Use plugins that highlight YAML syntax errors.
[Searching solution for a different question? We’re happy to help.]
Conclusion
By following these tips and fixes, we can resolve the error and ensure smooth Ansible playbook execution.






0 Comments