Linux presents various types of servers like Cloudlinux, CentOS, Ubuntu etc. Every server type has its own merits and demerits.
And, the choice of the server type depends on factors like purpose of the server, number of accounts etc.
This often confuses new server owners on the type of server to choose.
At Bobcares, we often get queries from such customers regarding server types in our Infrastructure Management services.
Today, let’s have a look on CentOS vs CloudLinux servers.
CentOS vs CloudLinux
CentOS is a robust operating system that has been hosting websites for many years now. It offers better performance when there are only few websites on the server.
CloudLinux on the other hand, comes as a best solution when you need to share resources among large number of websites.
Thus, both CentOS and CloudLinux has its own pros and cons. Let’s have a closer look at each of them.
1. Stability
When coming to Web Hosting servers, stability is of great importance. In CloudLinux servers, there is option to limit resources allotted to a particular user. As a result, in a shared server, no single user can overload the server. This is a great advantage when there are many websites hosted on the same server.
CentOS has been around for a while now in the Hosting industry. It is efficient in handling few websites that requires high resource usage.
Thus, in case of stability in shared hosting, CloudLinux gets an upper edge.
2. Usage Tracking
Similarly, in shared hosting, the resource usage by each website is really critical to manage the server resources wisely. We cannot allow a single website to eat up all the processing power of the server and make other websites slow.
It is a Web Hosting provider’s responsibility to ensure that customers receive the resources that they pay for. Since CloudLinux tracks resource usage of each user, it helps providers to suggest package upgrades if needed.
Another advantage is that, CloudLinux beautifully integrates into domain management panels like cPanel. And, this provides users detailed graphs on exact usage of their applications.
The user manager interface on cPanel CloudLinux server looks like :
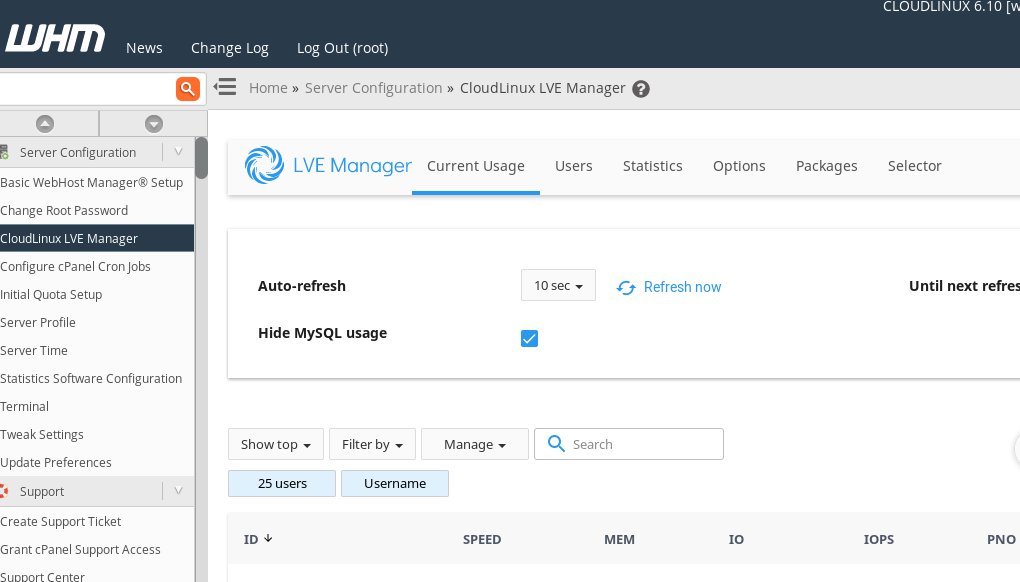
But in CloudLinux, this resource restriction often has a downside too. If a website run multiple php scripts or heavy processes, it will often get errors like “resource limit reached”. And this needs close monitoring and upgrade to higher usage limits.
In the case of CentOS servers, there is no built-in system for user resource usage tracking. We need to install separate applications like psacct, monit etc. to track the resource usage of each website.
3. Security
Another major factor that affects the choice of server type is security.
CloudLinux utilizes a technology called CageFS. This technology completely separates each user’s file system. So, a user cannot see another user’s files or processes. This is really helpful in shared hosting servers. All websites cannot be hacked due to one account being compromised.
But, this is not the case in CentOS. If an attacker enters the server via a weak website, it can typically modify server files and harm the entire server.
Fortunately, CentOS also provides timely security patches that are really easy to install. They typically rule out all the security flaws. But we need to make sure that all website applications are secure. Our Hosting Support Engineers set up a decent firewall system on CentOS server, ensures timely updates and this helps to effectively defend attackers.
4. Ease of Use
When you have set up the server, the real challenge lies in the maintenance of the server. Server hacks mainly happens in poorly maintained servers.
CloudLinux offers hundreds of additional features to make web hosting easier. An example would be the option to choose php version for each website.
Also, CloudLinux has its own packages. Updates are pretty simple with utilities like “yum”.
Similarly in CentOS, we can simple search application updates and install them via “yum”. There are options to automate package updates too.
In a nutshell, with minimal customization, both CentOS and CloudLinux scores almost equally when coming to the “ease of use” factor.
5. Costs involved
Just like any business, cost is a major factor in making decisions about the server too.
CentOS is fully free of charge.
But, CloudLinux needs a license. As of now, a single license costs around $14/month. But, there are discounts for getting licenses in bulk.
Considering the purpose of the server, typical visitors, target customers, one can go for either free CentOS or for paid CloudLinux. When you own a VPS, where you do not want to limit resources for your own sites, CloudLinux may not be needed.
Conclusion
Evaluating the merits and demerits of CentOS and CloudLinux, a final word largely depends on the purpose of the server. That’s why, our Security Engineers usually opts for CentOS server when having only few websites. And for shared hosting, CloudLinux proves to be a better option.







CloudOS does not cost $14, it cost $14/Month
Hello Manuel,
Thank you. Pricing is corrected now.
Hello,
“Handle a few websites” who much is a few? 1-3 or -10?
Hello Marc,
Yes, when your server hosts less than 10 websites. Again, the individual resource usage of each site also can be a factor.
Thanks so much for this informations about cloudlinux .
I’m new use for cloudlinux.
Can you please write an article on Almalinux? Hope it will be super cool. But honestly speaking, I’ve no clear idea about it.