Trying to find a solution for ‘MySQL Workbench error 61’? Here’s how we fix it.
MySQL Workbench is the best option to use when it comes to graphical management in MySQL.
At Bobcares, we often receive requests to fix MySQL errors as a part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s explore more on this error and see how our Support Engineers fix it.
What causes MySQL Workbench error 61 to show up?
This error normally pops up when trying to use MySQL Workbench and connect through an SSH tunnel. And the error shows up when the SSH connection doesn’t complete successfully.
This error can occur due to different reasons. This includes entering an improper hostname, entering an incorrect password while connecting to the database, default MySQL port is occupied by some other process in the server.
For instance, the error appears as below,
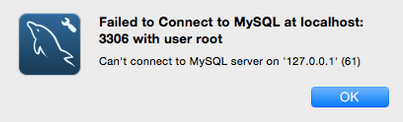
How we fix this MySQL Workbench error 61?
We have now discussed the cause of this error. Let’s now see how efficiently our Support Engineers fix this error.
1. Host error
Recently, one of our customers experienced some trouble in connecting to MySQL Workbench.
He received the below error message,
Can't connect to MySQL server on '127.0.0.1' (61)
Our Support Engineers started to troubleshoot this error by checking the configuration file my.cnf.
We opened the /etc/mysql/my.cnf in a text editor and commented the bind-address parameter line. We updated the below code
bind-address = 127.0.0.1
to
#bind-address = 127.0.0.1
After this, the connection was successful.
2. Port conflict
In another case, one of our customers got the same error but the fix was a different one. Here, we checked that the bind-address was already commented and it was not a problem with the host.
So, we investigated further by checking the port of MySQL. We checked it by using the below command:
netstat -plunt | grep 3306
Here, the result was not with MySQL. The server had MySQL running on a different port. So, we simply changed the port of MySQL from 3306 to 3307 by adding the below line in my.cnf file
port = 3307
And then restarted the MySQL service using the command:
service mysql restart
Finally, this fixed the error.
3. Firewall restrictions
Likewise, firewall restrictions on MYSQL port can also be a reason for the MySQL Workbench error 61.
The connection will work only when MySQL is running and allow connections from remote IP addresses. Thus, we always check local and external firewalls to make sure they’re allowing inbound connection at port 3306.
[Need any assistance with MySQL errors? – We’ll help you]
Conclusion
In short, the MySQL Workbench error 61 occurs when there are problems in completing the connection successfully. Today, we saw the causes like incorrect host settings, port conflicts, bad firewall, etc. and how our Support Engineers fix it.







Hey, thanks for the quick fix. I did notice a difference on the file and the path on Ubuntu 18.04 server. The path is /etc/mysql/mysql.conf.d/mysqld.cnf. The file is mysqld.cnf. All in all everything works great now. Thanks again.