Install Webmin FreeBSD with the help of our skilled Support Engineers.
At Bobcares, we deal with queries like these every day as a part of our Server Management Services.
Moving on, let’s find out how our talented in-house experts install Webmin on FreeBSD 12.
What is Webmin?
Webmin is an open-source web-based system tool that is used for Unix and Linux systems. You can use it to set user accounts, manage DNS servers, Apache web servers, mail servers, samba and File configuration, manage database servers, package management, and so on. The possibilities are endless.
Today, we are going to take a look at how to install Webmin on FreeBSD 12. This Webmin tutorial will answer all your queries.
Before we begin, our Support Team would like to point out that the package can be installed either by building Webmin from source or from binary repository. Here, we are going to go along with the binary installation.
How to install Webmin on FreeBSD?
FreeBSD comes with a package manager called pgk that can be used to install Webmin.
- First, we will update the FreeBSD package index with the following command:
# pkg update
- Then, install Webmin by running the following command:
# pkg install webmin
You will be prompted to answer whether you want to proceed or not, enter yes.
- After that, we will run the following command as root to configure Webmin
# /usr/local/lib/webmin/setup.sh
Our Support Engineers would like to remind you to set the following parameters:
- Log file directory
- Config file directory
- Full path to Perl
- Web server port (default: 10000)
- Login name(default: admin)
- Login password
- SSL option (Y/N)
How to start Webmin service on FreeBSD?
Now that Webmin has been installed and configured on FreeBSD, it is time to set Webmin service to start on boot:
- First, run the following command to start the Webmin service on system boot:
# sysrc webmin_enable="YES" webmin_enable: -< YES
This will add the last line to the /etc/rc.conf file.
- After that, run the following command to start Webmin service for the first time:
# service webmin start Starting webmin. Cron 15469220631494 missing any time spec
- The service will be listening on port 10000 as seen below:
# sockstat -4 -6 |grep 10000 root perl 1535 5 tcp4 *:10000 *:* root perl 1535 6 udp4 *:10000 *:*
How to access Webmin interface on FreeBSD?
-
- First, open the server URL or IP address port 10000. For instance: https://192.168.122.197:10000.
- In case you come across an invalid certificate message as seen below, click Continue Anyway.
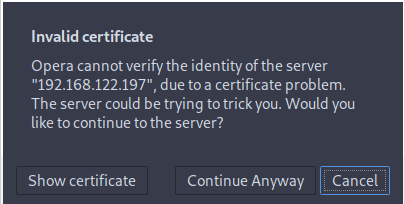
-
- Then login with the username and password specified during the installation.
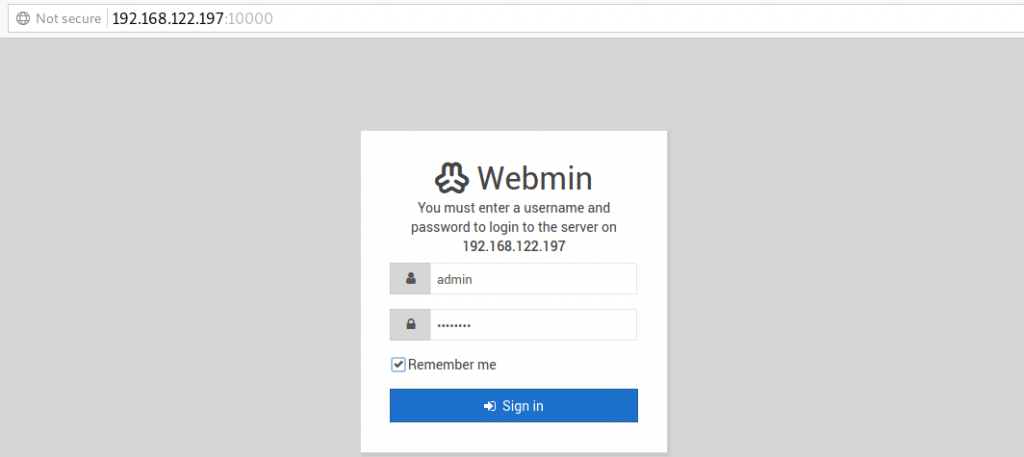
Now lean back and enjoy Webmin installed on your FreeBSD 12.
[Looking for help with Server Management? Give us a call today.]
Conclusion
To sum up, we learned how to install Webmin on FreeBSD 12 like a pro. Our Support Engineers took us through each step to ensure we enjoy seamless administration of FreeBSD from a web interface.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.







0 Comments