Complete tutorial to Install Redis® on Debian 12.11 with security tips. Our Redis Support team is ready to assist you.
Install Redis® on Debian 12.11
Redis® is a fast, open-source in-memory database used for caching, messaging, and real-time apps. It supports various data types and offers replication, persistence, and clustering for reliability.
This article covers Redis®’s key features, installation, configuration, security, and how to access and use it via CLI.
What is Redis®?
Redis is a blazing-fast, open-source in-memory database that powers caching, messaging, and real-time apps. It handles strings, hashes, and lists effortlessly while offering replication and disk persistence for reliability. Trusted for instant data access, Redis is perfect for web caching, session management, and analytics.
Key Features of Redis®
Redis is an open-source, in-memory data store used as a database, cache, and message broker. It keeps data in RAM, making it very fast for reading and writing. Redis supports many data types like strings, lists, sets, and hashes, which makes it easy to handle different kinds of data. It also saves data to disk, so your information is safe even if the system restarts.
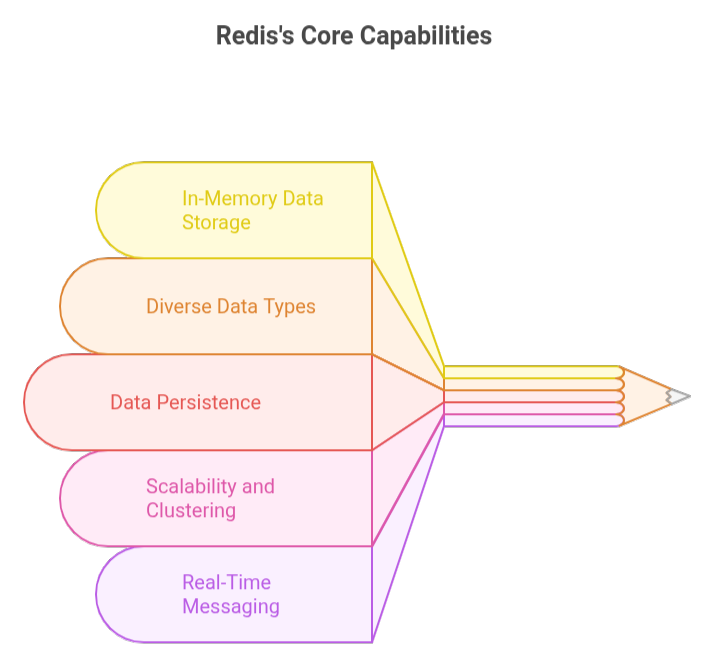
Redis is designed for high performance and can handle millions of operations per second. It includes features like automatic failover, clustering for large-scale data, and real-time messaging. Redis also supports transactions, scripting, and extra modules, giving developers flexibility to build fast, reliable, and scalable applications.
How to Install Redis® on Debian 12.11
- First, update your system’s package list and upgrade existing packages to ensure compatibility:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y- Install Redis from the official Debian repositories:
sudo apt install redis-server -y- Check that Redis installed correctly by confirming the CLI version:
redis-cli --version- Make sure Redis starts automatically on boot and is currently running:
sudo systemctl start redis
sudo systemctl enable redis- Use the Redis CLI to ensure the server is operational:
redis-cli pingA successful response will return:
PONGFor more advanced installation options, check out our guide on installing Redis 4.x from source on Linux.
Configuring Redis on Your Server
- Configuration File (redis.conf)
- Location: /etc/redis/redis.conf (Redis 8+: redis-full.conf)
- Key Settings: port, bind, daemonize, dir, dbfilename, save, appendonly, maxmemory, maxmemory-policy
- Apply Changes:
sudo systemctl restart redis- Runtime Configuration
- Temporary Changes:
redis-cli CONFIG SET maxmemory 1gbPermanent Changes:
redis-cli CONFIG REWRITELearn how to uninstall Redis from Ubuntu and remove all related files and settings.
How to Secure Redis®?
By default, Redis does not require authentication, which can expose it to unauthorized access. Follow these steps to secure your Redis server:
- Enable Password Authentication
Edit the configuration file:
sudo nano /etc/redis/redis.confUncomment and set a strong password:
requirepass YourStrongPassword- Create Standard Users
Add a limited-access user to restrict dangerous commands:
user db_client on +@all -@dangerous ~* >StrongPassword- Restart Redis
Apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart redisCheck out our guide on using Redis Bloom Filter commands for more insights.
How to Access Redis®?
- Open Redis CLI:
redis-cli- Ping the server (without authentication):
127.0.0.1:6379> pingIf authentication is enabled, this will return:
(error) NOAUTH Authentication required.
- Authenticate as the default user:
127.0.0.1:6379> auth <your_password>- Authenticate as a standard user (if created):
127.0.0.1:6379> auth db_client <user_password>- Test commands:
Create a key:
127.0.0.1:6379> set hello "Greetings from Redis!"Retrieve the key value:
127.0.0.1:6379> get hello- Exit the CLI:
127.0.0.1:6379> exitRead our guide to quickly resolve the “unable to find a match” error in Redis.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In short, Redis® provides a fast and reliable solution for caching, messaging, and real-time data needs. By following the steps outlined in this guide, you can easily install Redis on Debian 12.11 and configure it for secure and efficient use in your applications.
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to fix the “554 5.7.1 : Relay access denied” error.







0 Comments