When a single SSL certificate is shared by multiple websites, the browser triggers the error 421 misdirected request. It happens due to the conflicts in the virtual host entry.
At Bobcares, we help our customers fix similar SSL errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s take a closer look at how to fix this error.
What causes the ‘421 misdirected request’ error?
When a single TLS certificate is shared across many domains, the certificate either has a wildcard name, such as ‘*.example.org’, or carries several alternate names. Browsers using HTTP/2 recognize that and reuse an already opened connection for such hosts.
But when there are multiple requests for multiple hosts on the same TLS connection, renegotiation becomes impossible. It may then trigger the error “421 Misdirected Request”, to the client.

How to fix ‘421 misdirected request’?
Here are some of the common methods that can be used to fix the issue include:
- Using Separate SSL for each domain
- Disabling HTTPS redirection
- Clearing browser cache
1. Using Separate SSL for each domain
As indicated earlier, usage of a single SSL certificate within multiple domains commonly triggers the misdirected request error. This commonly happens when HTTP/2 tries to reuse the connection request.
Thus to fix this error, the reuse of connection by HTTP/2 should be stopped. Using separate SSL for each domain will help to avoid reusing the connection by HTTP/2.
Another method is to move each domain to a different IP address. This will also help to avoid the reuse of connection requests.
2. Disabling the https redirection code
As this error happens after enabling SSL over multiple domains with the same certificate, the cost-effective fix in this situation would be to disable the http:// to https:// redirection. However, this is not a recommended solution.
But in case some of the domains sharing the certificate are more like personal sites and do not contain any sensitive information, not everyone would like to purchase a separate certificate for it. In such cases, to make the website back online, a stop on the http:// to https:// redirection will help.
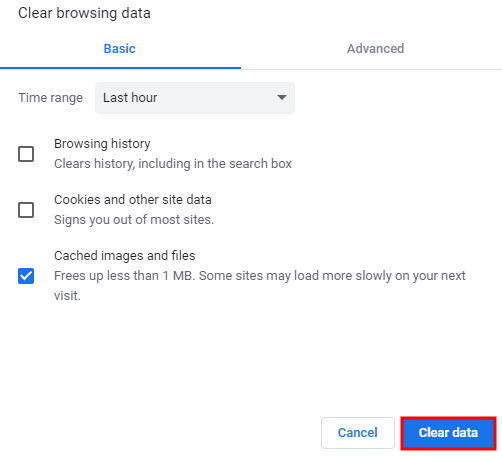
3. Clearing the browser cache
At times, it could be a simple browser cache. It is possible for the browsers to cache the 421 response. Thus it is not a bad idea to try clearing the browser cache.
[Still having the problem with 421 misdirected request fix?- We’re available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In short, conflicts in the virtual host entry triggers the 421 misdirected request when the server shares a single SSL certificate within multiple domains. Today, we saw how our Support Engineers fix this error.







This article helped me a lot. Thanks!