Is your Nagios showing ‘check_nrpe socket timeout after 10 seconds‘ error?
Usually, this happens due to the port or IP address block either in Nagios core server or host server.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from our customers to fix these Nagios errors as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, let’s get into the details on how our Support Engineers fix this by whitelisting IP/port in the servers.
What causes the check_nrpe socket timeout after 10 seconds?
Let’s begin by checking the error in detail.
In general, Nagios monitoring servers use the check_nrpe plugin to monitor the service states in a remote server.
The timeout indicates how long the check_nrpe command on the Nagios core will wait for a response from the NRPE agent.
The default value of timeout is 10 seconds which is a small value for certain checks.
From our experience in managing Nagios, the major cause of the error can be blocking of IP/port in the server, closed 5666 port, etc. Other reasons include bad nrpe timeout settings or failed NRPE daemon.
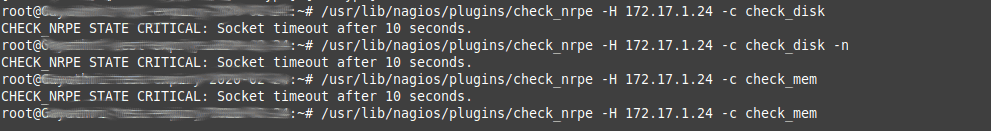
In all cases, the error appears in the monitoring system(Nagios) as follows.

The error obtained from the backend of the Nagios server.
Steps to fix ‘check_nrpe socket timeout after 10 seconds’!
At Bobcares, where we have more than a decade of expertise in managing servers, we see many customers face the same error.
Now, let’s see how our Support Engineers fix this error.
Verifying NRPE status
We begin by checking whether NRPE is running on the remote host. If NRPE runs as under xinetd, we check its status by
service xinetd status
Or if it runs as NRPE daemon, we check the process status using:
ps ax | grep nrpe
And, when they are not running, we simply restart it.
Nagios timeout
Likewise, we ensure that the timeout settings at the Nagios server do not cause the error.
We modify the check_nrpe timeout on the Nagios server. As a result, the check_nrpe command on the Nagios server will wait for a response from the NRPE agent for the specified time. This avoids timeout errors even when there is a delay in response.
Checking Remote Host’s Ports and Configuring IPTables
As we already saw, the most probable reason for the error will be firewalls and port 5666 blocks. The error is obtained when NRPE traffic is not allowed in the firewall. Similarly, if port 5666 is not open on the host firewall, the same error pops up.
Frequently many customers approach us with the same error, we handle it by following the below steps.
1. Initially, we confirm whether the port 5666 is open on the remote host.
NRPE’s port settings will be available from the /etc/services file.
2. We check this by running check_nrpe from the remote host to itself.
After that, we also make sure by logging into the remote host as root and run the following command.
/usr/local/nagios/libexec/check_nrpe -H localhost
On success, we then get an output as follows.
NRPE v2.15
If it is not the output, then we make sure to open port 5666 on the remote host’s firewall. This again depends on the server firewall too.
1. Configuring IPTables
We have to open port 5666 on the host firewall, according to the firewall used. In most Linux distributions, we use IPTables.
To get a listing of the current IPTables rules, we run the following on the remote host as root:
iptables -L
The expected output is
ACCEPT - tcp -- 0.0.0.0/0 0.0.0.0/0 tcp dpt:5666
OR
ACCEPT tcp – anywhere anywhere state NEW tcp dpt:nrpe
If the port is not open, we then add an IPTables rule for it using the following commands:
iptables -I INPUT -p tcp --destination-port 5666 -j ACCEPT
service iptables save
These commands work for TCP/IPv4.
Similarly, for ipv6 we use the following ones.
ip6tables -L
ip6tables -I INPUT -p tcp --destination-port 5666 -j ACCEPT
service ip6tables save
2. Adding rules to Firewalld
On CentOS servers, there will be Firewalld running on the server. Therefore, we need to add rules in Firewalld.
For getting the list of the current Firewalld rules, we run the following on the remote host as root:
firewall-cmd --list-all
The expected output is as follows.
ports: 5666/tcp
If the port is not found open, then we add a Firewalld rule for it by using the following commands:
firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp firewall-cmd --zone=public --add-port=5666/tcp --permanent
Then, Firewalld applies to both TCP/IP v4 and TCP/IP v6.
That fixed the problem and Nagios checks start working again.
[Still having the problem with check_nrpe socket timeout after 10 seconds?- We’re available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In short, check_nrpe socket timeout after 10 seconds error happens due to IP address or port restrictions, bad timeout values, etc. Today, we saw how our Support Engineers help the customers to fix this error.







0 Comments