‘Couldn’t Update the System Reserved Partition’ on Windows triggers since the SRP is smaller in previous Windows versions.
As part of our Server Management Services, we assist our customers with several Windows-related queries.
Today, let us focus on the various aspects of System Reserved Partition on Windows.
What is System Reserved Partition
When we perform a clean OS install, Windows Installer creates a special System Reserved Partition (SRP) on the Master Boot Record (MBR) disk partition table.
This is a hidden partition with the NTFS file system, which is not assigned a drive letter by default and does not appear in File Explorer.
In Windows 7/Windows Server 2008 R2 the size of the System Reserved partition is 100 MB, in Windows 8.1/Windows Server 2012 R2 it is 350 MB, and in Windows 10/Windows Server 2016 it is increased to 500 MB.
The System Reserved Partition in Windows
First, let us find the location of the System Reserved partition and how to view its contents.
Run the Computer Management,
mmc snap-inThe following volume attributes are assigned to the SRP:
Primary partitionActiveSystemThe System Reserved partition is only present on BIOS computers or UEFI devices that have the Legacy Compatibility Support Module (CSM) enabled.
We use the MBR (Master Boot Record) partition table on the system disk of such computers. On computers with UEFI in native mode and GPT partition table, there is no SRP partition.
By default, the SRP does not assign a drive letter. We can set the drive letter through the Disk Management Console (
diskmgmt.mscGet-Partition -DiskNumber 0 -PartitionNumber 1|Set-Partition -NewDriveLetter R
This is how the contents of the System Reserved volume look like:

If we are installing Windows to a disk with existing partitions, the installer does not create a separate 500 Mb System Reserved partition.
In this case, the Boot Manager bootloader files are on the same volume where Windows is.
Use of System Reserved Partition on Windows
In earlier versions of Windows, boot files were on the partition with the installed OS.
Starting with Windows 7, MSFT developers added a separate hidden System Reserved partition to store bootloader files. This solution helps to protect the bootloader files from users and improve the stability of Windows.
The System Reserved partition contains:
- Windows bootloader (bootmgr), and a file with the bootloader configuration BCD (Boot Configuration Data)
- Service data of the BitLocker encryption subsystem
- Windows Recovery Environment (WinRE) files to troubleshoot various boot problems
- System Volume Information folder for system recovery points metadata
- BOOTNXT – to boot Windows from USB flash drives (for example, for Windows To Go)
- BAK – a backup of the boot sector used on MBR disks.
Can we Delete the System Reserved Partition on Windows?
We should not delete the SRP without a good reason, and even more so to save disk space (500 MB is not so much).
Without this partition, Windows will not be able to boot. If the boot partition with the bootloader configuration is missing, errors may appear:
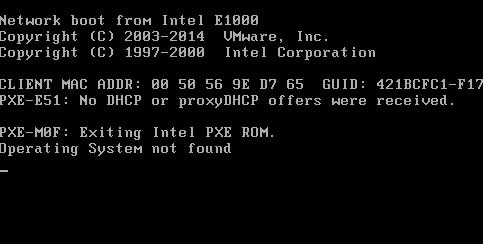
or
In this case, we have to manually restore the Windows bootloader and place it on the system drive C.
How to Create a System Reserved Partition Manually in Windows
If we delete the SRP (or it is initially missing) and want to restore it, we follow these steps:
- Use the
tool to shrink the Windows partition by 500 MB (For example, here we assume Windows is installed on partition 1):diskpart
diskpart list volume select volume 1 shrink desired=500
- Create a new 500 MB NTFS partition:
create partition primary format fs=ntfs active assign letter R exit
- Then, place the Windows bootloader files on the new partition:
bcdboot C:\windows /s R: bootrec /fixmbr bootrec /fixboot bootrec /rebuildbcd
However, in most cases, it is easier to move the bootmgr configuration to the Windows system partition.
[Finding it hard? Don’t worry, We are here for you.]
Windows can’t boot after Accidentally Deleted SRP
If other partitions prevent us from shrinking/extending the Windows volume, we can restore the bootloader configuration and place it on the partition where Windows is installed.
Let us take a look at the steps our Support Engineers follow to fix Windows boot after deleting an SRP:
First, we cross-check that the System Reserved partition is missing from any Windows boot/installation media (USB flash drive or DVD).
On the installation screen, we press Shift+F10 to open a command prompt. Run
diskpartlist volume
As we can see, the SRP is missing, and of course, the Windows cannot boot from this disk.
In this case, to restore the system, we need to recreate the bootloader entries.
In order not to create the separate 500 MB SRP, the
bootmgrHence, we run the following commands in WinPE command prompt to place the boot environment files on drive C:\ and specify the path to the Windows directory:
bcdboot c:\windows /s c:If successful, the command will return Boot files successfully created.
Furthermore, we need to overwrite the boot sector:
bootsect.exe /nt60 All /forceIf the error “Element not found” appears, try to make the system partition active using
.diskpart
Then, make the C:\ partition active. To do it, we execute the following commands:
diskpart
list disk
select disk 0
list partition
select partition 1
activeNote: we should see the message “DiskPart marked the current partition as active“
exitFurthermore, we run the below commands one by one:
bootrec /fixmbr
bootrec /fixboot
bootrec /scanos
bootrec /rebuildbcdThe third command will scan all disks and try to find installed Windows copies. In our example, the OS is in the C:\Windows folder. The system will ask to add these Windows entries to the boot list. Confirm it.
Finally, restart the computer and make sure that Windows is booted correctly. Make sure that
bootmgr
“Couldn’t Update the System Reserved Partition” on Windows 10
When upgrading from Windows 7/8.1 to Windows 10 (or when upgrading to the new Windows 10 build), we may receive 0xc1900104 or 0x800f0922 errors:

This is because the SRP is small in previous Windows versions than in Windows 10. Generally, if the SRP is full and there is not enough free space (at least 15 MB) to place the Windows bootloader system files, we will get this error.
In this case, Microsoft recommends deleting the font files from the R:\Boot\Fonts directory to free up space on the SRP or we can try to expand the SRP using any third-party partition manager tool on a bootable USB stick.
[Need help to manage SRP in Windows 10? We are available 24*7]
Conclusion
To conclude, System Reserved Partition is a hidden partition with the NTFS file system, which is not assigned a drive letter by default. Today, we saw how our Support Techs go about the error, Couldn’t Update the System Reserved Partition on Windows







0 Comments