Learn more about the KernelCare Extension for Plesk. Our Plesk Support team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
How to Validate and Install the KernelCare Extension for Plesk
Today, we are going to take a walk through the steps to ensure that the KernelCare extension is properly licensed and installed on our Plesk instance. Additionally, we’ll cover troubleshooting common issues that may arise after installation.
An Overview:
- Why Use KernelCare for Plesk
- Step 1: Validate Plesk Additional License Keys
- Step 2: Install the KernelCare Extension
- Step 3: Verify the KernelCare Installation
- Troubleshooting KernelCare Installation Issues
- Issue: KernelCare Extension Hangs After Installation
- Issue: Daily Email Notifications for Expired Trial License
- Common Errors and Solutions
- Best Practices for KernelCare on Plesk
- Monitoring and Managing KernelCare Performance
Why Use KernelCare for Plesk
KernelCare offers a crucial advantage for Plesk users by enabling zero-downtime kernel updates. This ensures that our server remains operational during updates without needing reboots. This is handy for businesses requiring high uptime. It also enhances security by quickly applying patches to kernel vulnerabilities, reducing the risk of exploits.
Additionally, it cuts maintenance costs by minimizing server downtime and automating updates. Hence, it is a time-saving tool for administrators. For Plesk users managing multiple sites or services, KernelCare significantly boosts efficiency and security.
Step 1: Validate Plesk Additional License Keys
Before installing the KernelCare extension, let’s ensure our Plesk license includes the required KernelCare extension. Follow these steps to verify:
- First, log into Plesk.
- Then, go to Tools & Settings.
- Next, head to License Management.
Now, check if “ext-kernelcare-plesk” is listed on the License Management page. If it is, our license is properly configured, and we can proceed with the installation.
If we don’t see the KernelCare license key, follow these steps:
- Log in to the client area billing account.
- Then, go to the VPS or Dedicated Server subscription.
- In the left panel, click on Addons under the Overview section.
- Next, find the KernelCare addon and copy the Product Key.
- After that, return to Plesk, go to Additional License Keys, and insert the copied Product Key.
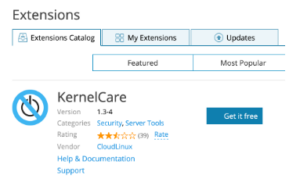
Step 2: Install the KernelCare Extension
Now that our license is validated, follow these steps to install the KernelCare extension:
- Log into Plesk.
- Then, click on Extensions from the left sidebar.
- Next. search for the KernelCare extension.
- Then click Get it free to install the extension.
Step 3: Verify the KernelCare Installation
Once KernelCare is installed, we can verify its functionality by checking the kernel versions:
- Open the KernelCare extension.
- Also, make sure that the Effective Kernel Version is higher than the Real Kernel Version. This indicates that KernelCare is properly applied and functioning.
Troubleshooting KernelCare Installation Issues
Issue: KernelCare Extension Hangs After Installation
If we are unable to access KernelCare after installation and the following message is displayed indefinitely, there might be an issue on KernelCare’s side.
The KernelCare extension has been successfully installed. Please allow up to 5 minutes for all components to be fully configured.
Fix:
- Log into the server via SSH.
- Then, remove the following lock files:
rm /opt/psa/var/modules/kernelcare-plesk/installing.lock rm /usr/local/psa/var/modules/kernelcare-plesk/installing.lockCopy Code - Re-install the KernelCare extension with the following commands:
plesk bin extension -u kernelcare-plesk plesk bin extension -i kernelcare-pleskCopy Code
Issue: Daily Email Notifications for Expired Trial License
In some cases, we will get daily email notifications from KernelCare’s cron task stating:
The IP 203.0.113.2 was already used for trialing.
This occurs when the KernelCare trial license has expired, or the extension was removed but the cron task persists.
Fix:
- If we have a valid KernelCare license, update it in Tools & Settings > License Management > Retrieve Keys.
- If we no longer need KernelCare, we can remove the extension:
- To remove KernelCare via Plesk:
-
- Log into Plesk.
- Go to Extensions > My Extensions > KernelCare.
- Click Remove.
-
- To remove KernelCare via command-line:
- Connect to the server via SSH.
- Remove the KernelCare extension:
plesk bin extension -u kernelcare-pleskCopy Code
- To remove KernelCare via Plesk:
- Remove the KernelCare package:
Common Errors and Solutions
Even though KernelCare is generally reliable, here are some common issues:
- If the KernelCare key is missing in Plesk, retrieve it from our billing account and apply it in License Management.
- If the installation seems stuck, remove the lock files via SSH and reinstall the extension using the command line.
- If we receive trial license expiry emails, update our license in License Management or remove the extension if no longer needed.
Best Practices for KernelCare on Plesk
To optimize KernelCare:
- Ensure KernelCare auto-updates are enabled in Extensions to maintain security without manual intervention.
- Regularly check the kernel status in Extensions to verify that updates are applied correctly.
- Furthermore, periodically review KernelCare logs in `/var/log/kcare/` to detect issues early.
- Always maintain regular server backups to prevent data loss in case of failures.
- Additionally, complement KernelCare with other Plesk security tools like ImunifyAV for full protection.
Monitoring and Managing KernelCare Performance
To keep KernelCare functioning optimally:
- Use the Plesk interface or run `kcarectl –info` via SSH to check KernelCare’s status.
- Regularly review logs in `/var/log/kcare/` for insights into kernel updates and potential issues.
- Additionally, configure email notifications in **Tools & Settings** to stay informed about important updates.
- Perform periodic audits using Plesk tools and external monitoring solutions to ensure updates aren’t causing issues.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
By following the above steps, we can ensure that the KernelCare extension is properly licensed, installed, and configured on our Plesk instance.
Additionally, we now have the tools to troubleshoot common issues that might arise after installation, ensuring our server’s kernel stays up-to-date and secure without reboots.
In brief, our Support Experts introduced us to the KernelCare Extension for Plesk.




0 Comments