Easily change the DocumentRoot in Apache to organize and manage your website files. Our Apache Support team is ready to assist you.
Change the DocumentRoot in Apache
The primary directory where the files for your website are kept is the Apache DocumentRoot. Apache retrieves files from this location when users visit your website. It points to /var/www/html by default, but you can modify it at any moment. You have more freedom to plan projects and handle websites with ease via this.
Introduction to Apache DocumentRoot
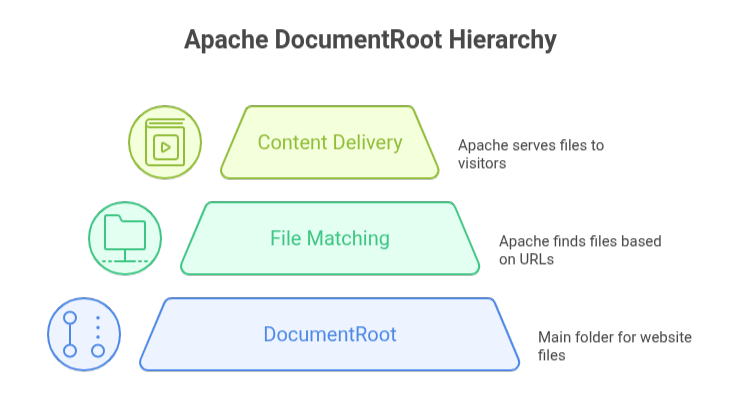
The Apache DocumentRoot sets the main folder where the Apache web server looks for website files to serve to visitors. A file within the DocumentRoot is matched by Apache when a URL is visited. For instance, if a user asks http://www.example.com/images/logo.png and DocumentRoot is /var/www/html/, Apache will deliver the file at /var/www/html/images/logo.png if it exists and has the required permissions.
Because it establishes a foundation for all online content on a server or virtual host, the DocumentRoot is an essential component of Apache setup. Typically, it is configured in a virtual host configuration or in the primary Apache configuration file, such as httpd.conf or apache2.conf.
How to Change the Document Root in Apache
Changing the Document Root in Apache is an essential step when organizing your server or creating a new website. Apache searches for the website files it provides to users in the Document Root directory. It is typically set to /var/www/html by default, but you can modify it to any location that works for your project’s architecture.
You may easily and safely modify Apache’s Document Root by following this step-by-step tutorial.
- Stop Apache Service
sudo systemctl stop apache2
# or
sudo service httpd stop- Create a New Document Root Directory
sudo mkdir -p /path/to/your/new/document/root- Update the Virtual Host Configuration
cd /etc/apache2/sites-available/
sudo nano 000-default.confChange the DocumentRoot directive and update the <Directory> block:
DocumentRoot /path/to/your/new/document/root
<Directory /path/to/your/new/document/root>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>- Set Permissions for the New Directory
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /path/to/your/new/document/root
sudo chmod -R 755 /path/to/your/new/document/root- Restart Apache and Verify
sudo systemctl restart apache2
# or
sudo service httpd restart
Open your site in a browser to confirm the new document root is working.Learn how to gracefully restart Apache2 and tweak its Debian configuration.
Troubleshooting Tips for Apache DocumentRoot Changes
- Check Configuration and Restart
Test syntax:
apachectl configtest
# or
httpd -tRestart Apache to apply changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2 # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo systemctl restart httpd # CentOS/RHEL- Fix Permissions and Ownership
- Set directory permissions:
sudo chmod -R 755 /path/to/new/documentrootSet file permissions:
sudo chmod -R 644 /path/to/new/documentroot/*
Ensure Apache owns the folder:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /path/to/new/documentroot # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo chown -R apache:apache /path/to/new/documentroot # CentOS/RHEL- Handle SELinux (CentOS/RHEL only)
sudo semanage fcontext -a -t httpd_sys_content_t "/path/to/new/documentroot(/.*)?"
sudo restorecon -Rv /path/to/new/documentroot- Check Apache Error Logs
Look for errors in:
/var/log/apache2/error.log # Ubuntu/Debian
/var/log/httpd/error_log # CentOS/RHEL- Verify Virtual Host and PHP Settings
Ensure the DocumentRoot is inside the correct <VirtualHost> block.
Check for conflicting DocumentRoot entries.
If using PHP, confirm doc_root in php.ini matches the new directory.
- Clear Browser Cache
Clear your browser’s cache so it loads the site from the new document root, not the old one.
Easy methods to solve the Apache no listening sockets available error.
Steps to Change Apache DocumentRoot in Linux
- Find the Configuration File
- RHEL/CentOS: /etc/httpd/conf/httpd.conf
- Ubuntu/Debian: /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.conf (or another .conf file in sites-available)
- Edit the Configuration
Open the config file with a text editor:
sudo nano /etc/apache2/sites-available/000-default.confChange the line:
DocumentRoot "/var/www/html"to your new location, e.g.:
DocumentRoot "/home/user/public_html"- Fix Permissions
Set ownership and permissions for the Apache user:
sudo chown -R www-data:www-data /path/to/new/document/root # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo chown -R apache:apache /path/to/new/document/root # RHEL/CentOS
sudo chmod -R 755 /path/to/new/document/root- Configure <Directory> Block (if needed)
If the new folder is outside the default web directory, add:
<Directory /path/to/new/document/root>
Options Indexes FollowSymLinks
AllowOverride All
Require all granted
</Directory>- Restart Apache
Apply the changes:
sudo systemctl restart apache2 # Ubuntu/Debian
sudo systemctl restart httpd # RHEL/CentOS- Verify
Open your site in a browser to confirm it’s loading from the new document root.
Quick solutions for the AH01630 Apache error on your server.
Handling Permissions and Mounted Partitions on Linux
It’s crucial to set the correct permissions when mounting a partition in Linux. Users may have security or access issues if they do not have the appropriate permissions. Here are a few easy ways to deal with it.
- Mount with User and Group Permissions
You can mount a partition so it belongs to a specific user and group.
In /etc/fstab:
UUID=your_partition_uuid /mnt/data ext4 defaults,uid=1000,gid=1000 0 2
Or mount manually:
sudo mount -o uid=1000,gid=1000 /dev/sdXY /mnt/data- Change Permissions After Mounting
If needed, adjust permissions after mounting:
- Give owner and group full access:
chmod -R 775 /mnt/dataChange owner and group:
chown -R your_username:your_groupname /mnt/dataFor detailed control, use ACLs:
setfacl -m u:username:rwx /mnt/data- Special Case: NTFS Partitions
On NTFS partitions, Linux permissions may not work well. Install ntfs-3g and mount with options in /etc/fstab to manage access properly.
- Mount Point Permissions
Before mounting, keep the mount point (like /mnt/data) restricted to root. Once mounted, the partition’s permissions control access.
Step-by-step guide to migrate your website from Apache to Nginx on Ubuntu.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
Learning how to change the DocumentRoot in Apache gives you full control over where your website files are stored and served. By updating the configuration, setting correct permissions, and restarting the service, you can easily customize your server setup to fit your project’s needs.
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to fix the “554 5.7.1 : Relay access denied” error.







0 Comments