SQL error 2627 is a common error that triggers during database restorations. It generally happens when the backup file contains a sequence object that is created by using the cache option in Microsoft SQL Server 2012
As a part of our Server Management Services, we help our Customers to fix SQL related errors regularly.
Let us today discuss the possible causes and fixes for this error.
What causes the SQL error 2627?
The SQL error 2627 triggers commonly on tables that contain PRIMARY KEY constraint. Whenever we try to insert a new record into such tables and the key of the record being inserted already exists in the table, it triggers the 2627 error.
It generally happens when the cached sequence created by the cache option in Microsoft SQL Server 2012 is flushed incorrectly during the database backup. This makes the value of the cached sequence larger than the value on the disk.
Thus when restoring the database with that backup, it shows the error message:
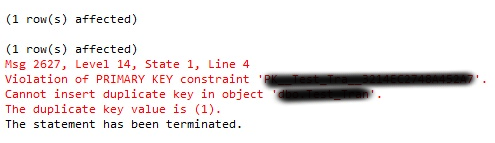
Another possible reason for it can be a bug in the spool and spool is generating more than expected rows. Let us now look into the steps to fix the violation of primary key constraint error.
How to fix the SQL error 2627?
To fix SQL Server Error 2627 you can use the Cumulative Update 4. It is recommended that you should use the most recent cumulative update that contains the hotfix.
Another possible fix would be to find the duplicate records in the database and remove them. We would need to use an SQL query for this purpose. The exact query to be used varies based on each scenario. For instance, a simple query to find if duplicates exist in a table would be:
SELECT username, email, COUNT(*) FROM users GROUP BY username, email HAVING COUNT(*) > 1
To display each of the duplicate rows, the format to be used would be:
SELECT a.* FROM users a JOIN (SELECT username, email, COUNT(*) FROM users GROUP BY username, email HAVING count(*) > 1 ) b ON a.username = b.username AND a.email = b.email ORDER BY a.email
The exact format of the query to be used varies based on the parameters in the table. Once the duplicate entry is identified, we can manually delete the duplicate ones using SQL Server Management Studio.
At times these steps may not help to fix the error completely and the violation error of the primary key constraint may remain the same. It happens only if the indexes were not created properly. In this situation, we need a backup plan of the database to restore the data.
Also, it is important to not rename an existing table as a backup of tables as this will leave the indexes in place which will prevent the recreation of the indexes during restoration.
[Need help to fix SQL errors? We are available 24×7]
Conclusion
In short, the SQL error 2627 triggers during database restorations when the backup file contains a sequence object that is created by using the cache option in Microsoft SQL Server 2012. Today we saw how our Support Engineers fix this error.







0 Comments