Using docker-compose, we can deploy ‘WordPress’ with Nginx, MySQL, and PHP-FPM. We will see how to proceed.
As part of our Docker hosting Service, Bobcares provides solutions to all queries, large and small.
Let’s take a look at how our Support engineers are dockerizing WordPress using Nginx and PHP-FPM.
How to Use Docker Compose to Install WordPress with nginx, php-fpm and mysql
Docker-Compose is a command-line tool that allows us to define and manage multiple Docker containers as a single service. Compose is written in Python. It can be installed with the pip command in Python.
We can run multiple Docker containers with a single command when using compose. It enables the creation of a container as a service. So, it is ideal for our development, testing, and staging environments.
Here, We’ll deploy ‘WordPress’ with Nginx, MySQL, and PHP-FPM using docker-compose. Each service will have its own container, which will be based on images from the Docker Hub Registry.
Install docker
We’ll start from scratch, manually installing docker and docker compose using the apt command.
- Firstly, make sure the Ubuntu repository is up to date. Then, install the latest updates:
sudo apt-get updatesudo apt-get upgrade
- Since docker is available by default in the Ubuntu repository, we can proceed to install it right away:
sudo apt-get install -y docker.io
- Start docker once the installation is complete. Then set it to start automatically during booting.
systemctl start dockersystemctl enable docker
- Finally, run the following command to test the Docker installation:
docker run hello-world
As a result, we’ll be able to see docker’s hello-world.
Install Docker-Compose
Docker-compose is available in the PyPI python repository because it is a python script. So, python pip can be used to install it. Hence, we must first install Python and Python Pip on our system.
- Firstly, Install python and python-pip by using these commands:
sudo apt-get install -y python python-pip
- Then, using the pip command, install docker-compose:
pip install docker-compose
- wait for the installation to complete. Then, use the docker-compose command to verify the installation:
docker-compose -v
As a result, we’ll get docker-compose.
Setup WordPress
The system now has docker and docker-compose installed. So, in this step, we’ll create and configure a Docker-compose environment for our WordPress project.
The ‘WordPress’ PHP application will be deployed as docker containers managed by docker-compose, with Nginx as the web server and MariaDB for the MySQL database. Each application will run in its own container, as shown in the following list:
- -nginx : We use the ‘nginx: latest’ official docker image.
- -WordPress : On docker-hub, WordPress provides some docker images. We’ll use latest wordpress with latest PHP-FPM on it.
- -MySQL : We’ll use the most recent version of MariaDB’s official container.
So, we require three docker images. We won’t run docker as root; instead, we’ll use a regular Linux user.
- So simply run the command below to create a new user.
useradd -m -s /bin/bash bobcarespasswd bobcares
- Add the user to the ‘docker’ group so that he or she can use the docker command. Then restart the docker service:
usermod -a -G docker bobcaressystemctl restart docker
- Log in as the ‘bobcares’ user. Then, for the WordPress project, make a new directory:
su - bobcaresmkdir -p wordpress-composecd wordpress-compose/
- Then, create a new directory for the project and a new file called ‘docker-compose.yml’. Simply type the following commands:
touch docker-compose.yml
mkdir -p nginx/
mkdir -p db-data/
mkdir -p logs/nginx/
mkdir -p wordpress/
File and Directory List of the project:
docker-compose.yml: It’s the configuration file, which we must create when starting a new project with Docker.
nginx: This directory contains our additional nginx configuration, such as the virtual host, and so on.
db-data: The data directory for mysql. ‘/var/lib/mysql’ data is mounted in the db-data directory.
logs: Application log, nginx, mariadb, and php-fpm are all stored in this directory.
wordpress: That directory will contain all WordPress files.
Now, create a new nginx configuration file for our wordpress virtual host in the ‘nginx’ directory.
- Firstly, create a new wordpress.conf file:
vim nginx/wordpress.conf - Then, copy and paste the following configuration:
server { listen 80; server_name wp-hakase.co;root /var/www/html;
index index.php;access_log /var/log/nginx/hakase-access.log;
error_log /var/log/nginx/hakase-error.log;location / {
try_files $uri $uri/ /index.php?$args;
}location ~ \.php$ {
try_files $uri =404;
fastcgi_split_path_info ^(.+\.php)(/.+)$;
fastcgi_pass wordpress:9000;
fastcgi_index index.php;
include fastcgi_params;
fastcgi_param SCRIPT_FILENAME $document_root$fastcgi_script_name;
fastcgi_param PATH_INFO $fastcgi_path_info;
}
} -
Finally, exit vim after saving the file.
Configure Docker-Compose
If we want to start the docker-compose project, we must first create the docker-compose.yml file, as shown below.
- With vim, edit docker-compose.yml:
vim docker-compose.yml
- Then, define our services, starting with Nginx on the first line. We’re using the latest version of the Nginx official docker image. We’ve set up port mapping from port 80 on the container to port 80 on the host.Then, configure the docker volumes for our Nginx virtual host configuration, Nginx log files volume, and the web root directory volume ‘/var/www/html’ next. The WordPress container is linked to the Nginx container.
nginx: image: nginx:latest ports: - '80:80' volumes: - ./nginx:/etc/nginx/conf.d - ./logs/nginx:/var/log/nginx - ./wordpress:/var/www/html links: - wordpress restart: always
- After that, we’ll need to specify the MySQL server. We’re using the most recent MariaDB image. Configure port 3306 for the container, and use the environment variable ‘MYSQL ROOT PASSWORD’ to set the MySQL root password. Finally, set up the MySQL data directory’s container volume.
mysql: image: mariadb ports: - '3306:3306' volumes: - ./db-data:/var/lib/mysql environment: - MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=Strong password restart: always
- Then, using the WordPress 4.7 docker image with PHP-FPM 7.0 installed, we’ll set up the WordPress service. Set the PHP-fpm port to 9000. Then enable the docker volume for the web directory ‘/var/www/html’ to the host directory ‘wordpress,’. Finally, configure the database using the WordPress environment variable, and then link the WordPress service to mysql.
wordpress:
image: wordpress:4.7.1-php7.0-fpm ports: - '9000:9000' volumes: - ./wordpress:/var/www/html environment: - WORDPRESS_DB_NAME=wpdb - WORDPRESS_TABLE_PREFIX=wp_ - WORDPRESS_DB_HOST=mysql - WORDPRESS_DB_PASSWORD=Strong password links: - mysql restart: always
- Finally, save the file and exit the vim editor after adding the three parts to the docker-compose.yml file.
Our docker-compose configuration is complete.
Run Docker-compose
- Begin by using Docker compose to create new containers. Start new containers based on our compose file in the wordpress-compose directory.
cd ~/wordpress-compose/docker-compose up -d - The command’s output can be viewed. There were three containers created. Let’s use the ps option to check the status of the container.
docker-compose ps - Moreover, if we want to see the container’s log output, use the commands below:
docker-compose logs nginx
docker-compose logs mysql
docker-compose logs wordpressInstall WordPress
- Let’s check the system’s available ports/open ports before moving on to the next step. Make sure we have three ports open: 80, 3306, and 9000.
netstat -tulpn
- Now open a web browser and type the server’s URL or IP address into the address bar.
http://serverIP/ - The WordPress installation page can be viewed. Select the preferred language and click ‘Continue.’

- After that, click ‘Install WordPress‘ and enter website’s title, admin user and password, and email address.
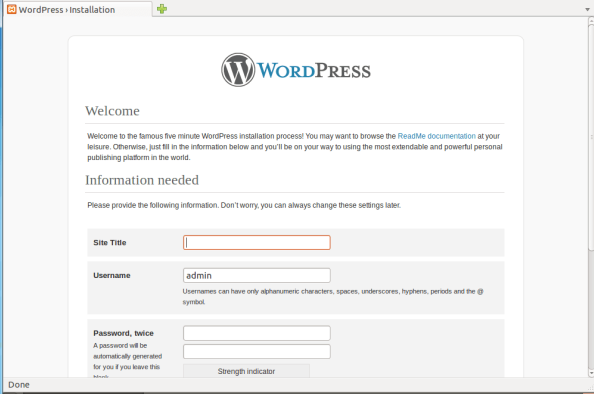
- The ‘WordPress Admin Dashboard‘ will be displayed.With docker-compose, WordPress was installed.
[Looking for a solution to another query? We are just a click away.]
Conclusion
To sum up, Bobcares skilled Support engineers demonstrated how to use docker compose to install WordPress with Nginx, MySQL, and PHP-FPM.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.








hi sir, setup i have one using this doc when i check the services in server its running fine but while i am trying to hit the ip on the internet its not working , my net is on and in security group of ec2 i have opened those 3 ports as well kindly help
Hi Tejaswini,
Please contact our support through live chat(click on the icon at right-bottom).