Brute force attacks are literally annoying and make the entire website down.
But, can we do anything to avoid this attack?
Yes. Popular control panels like Plesk offer Fail2ban aka IP Address Banning that protects websites from brute-force attacks.
However, problems like deprecated directives in the .htaccess file prevent the proper working of Fail2ban.
At Bobcares, we often get requests from our customers to configure Plesk brute force protection as part of our Server Management Services.
Today, we’ll see the reasons and how our Support Engineers configure brute force protection on Plesk and fix related errors.
How we set up Plesk to automatically ban IP addresses
IP address banning is an effective utility against brute-force attacks on a Plesk Linux server. It allows managing IP address banning on the server. Also, it monitors malicious signs like too many password failures, exploits, etc.
In order to perform IP address banning, we should install the Fail2Ban component on the server.
We use the following command to perform the IP banning manually,
For example,
plesk bin ip_ban --update -ban_period 120 -ban_time_window 120 -max_retries 3
Also, we set up Plesk to automatically ban IP addresses as follows.
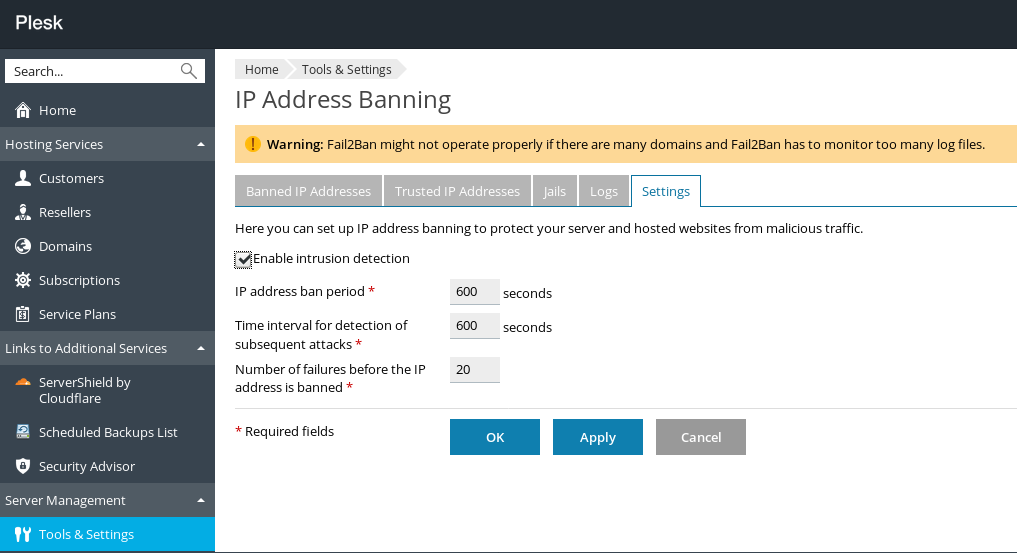
1. Initially, we go to Tools & Settings > IP Address Banning.
2. Then, we activate the Fail2Ban service by selecting the checkbox for Enable intrusion detection.
And, we fill the following settings:
- IP address ban period
- The time interval for the detection of subsequent attacks
- The number of failures before the IP address is banned
3. Finally, we click OK.
How we fix the errors related to brute force protection on Plesk
At Bobcares, where we have more than a decade of expertise in managing servers, we see many customers face problems while configuring brute force protection on Plesk.
Now let’s see how our Support Engineers fixed the top errors.
1. Deprecated detectives in the .htaccess file
Recently, one of our customers had a problem after setting up Fail2Ban on the server. Fail2Ban blocked visitors’ IP addresses after opening a website. And got an error
ERR_CONNECTION_TIMED_OUT.By investigating, we found the following error in the /var/log/fail2ban.log file.
fail2ban.actions [1343]: NOTICE [plesk-apache] Ban 181.xx.yy.2
This error happened due to the presence of deprecated detectives in the .htaccess file. Therefore, we searched for each .htaccess file inside the domain home folder and checked the deny directives in the .htaccess file.
To fix the error, we changed the code from
Order allow,deny Allow from all
To
Require all granted
This fixed the problem and IP banning started working fine.
2. Too many login attempts
Sometimes, a valid user IP can be blocked on the server when trying different passwords. This particularly happens in situations where the user can’t remember passwords.
Here, the user may get a Connection timed out message for mail, web, SSH, etc.
The error will look like:
ssh: connect to host server.hostname.com port 2022: Connection refusedThen, we check whether the IP address is blocked or not by using the following command.
iptables -n -L
Next, if it is listed we unban the IP address.
Moreover, we suggest customers enter the correct login details.
[Getting error after enabling brute force protection? We’ll fix it for you.]
Conclusion
In short, in order to strengthen the server security, we enable Plesk brute force protection on servers to prevent attacks. We also discussed the ways in which our Support Engineers fix related errors.








0 Comments