Follow simple steps to setup Node.js and NPM on Debian 12.11 quickly and easily. Our Server Management Support team is ready to assist you.
Steps to Setup Node.js and NPM on Debian 12.11
This article constitutes an overview of Node.js, its core features, and advantages such as its event-driven, non-blocking architecture and cross-platform interoperability. It also covers choosing the suitable Node.js version, specific methods to install Node.js and NPM on Debian 12, and how to test the installation to ensure everything works correctly. Read the article to comprehend all these crucial characteristics and start building powerful applications using Node.js.
What is Node.js?
Node.js is an open-source, cross-platform JavaScript runtime that is compatible with Linux, macOS, Windows, and other operating systems. It uses the V8 engine to run JavaScript code outside of the browser.
It enables command-line tools and dynamic web pages by allowing developers to use a single language for both frontend and backend development. Node.js’s event-driven, non-blocking I/O approach makes it scalable, lightweight, and perfect for real-time applications like gaming, chat, and streaming.
The OpenJS Foundation, a division of the Linux Foundation, is currently responsible for maintaining Node.js, ensuring open development and sustained maintenance.
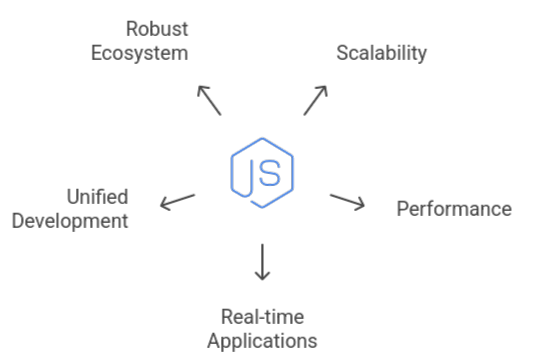
Key Features of Node.js
A JavaScript runtime environment called Node.js enables programmers to execute JavaScript on a server. It is popular for creating quick, scalable, and powerful programs for various operating systems, including Linux, macOS, and Windows.
Because it uses an event-driven, non-blocking I/O approach, it can process multiple requests simultaneously without waiting for a single task to complete. It supports thousands of connections while avoiding the complexity of multi-threading by managing many operations effectively via an event loop, despite only using one thread.
Although Node.js uses Google’s V8 engine, JavaScript is natively converted into machine code for fast and effective execution. It is perfect for real-time applications like chat systems, streaming platforms, and APIs that service a high number of users because of its speed and lightweight design.
Scalability is one of Node.js’s other main advantages. It can manage high traffic volumes and many simultaneous connections without experiencing performance problems via event loop and non-blocking I/O. In addition, thousands of pre-built libraries and modules are available to developers through its robust ecosystem, which is driven by NPM and streamlines and speeds up development.
Node.js integrates front-end and back-end development under a single language by supporting many platforms and enabling JavaScript to execute on the server. This helps teams work more quickly and effectively while also streamlining the development process.
Prerequisites
- An extensive knowledge of the variables, data types, operators, loops, conditionals, functions, arrays, and objects that make up JavaScript.
- Knowledge of asynchronous programming, including callbacks, promises, and async/await, because Node.js is an event-driven, non-blocking framework.
- Familiarity with arrow functions, classes, modules, template literals, and destructuring in contemporary JavaScript (ES6+).
- Writing cleaner and more effective code requires a basic understanding of functional programming concepts, such as closures and higher-order functions.
Learn everything you need here, and refer to our expert Vultr deployment guide for practical Node.js solutions.
Choosing the Right Node.js Version
Step 1: Use the version specified by your project at all times. Examine the documentation or the.nvmrc file to prevent errors and incompatibilities.
Step 2: Select the LTS (Long-Term Support) version for production applications. It is long-lasting, sturdy, and thoroughly tested.
Step 3: Use the Current (latest) version for experiments, personal projects, and testing new features. Just keep in mind that it can take some time for certain npm packages to catch up.
Install Node.js and NPM on Debian 12
- Using the Debian Repository (for stability, not latest version)
- Update your package list:
sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade -y- Install Node.js and npm:
sudo apt install nodejs npm -y- Verify installation:
node -v
npm -v- Using NodeSource (for the latest stable Node.js version)
- Install curl if needed:
sudo apt install curl -y- Set up the NodeSource repository (replace 22.x with your preferred version):
curl -fsSL https://deb.nodesource.com/setup_22.x | sudo -E bash -- Install Node.js and npm:
sudo apt install nodejs -y- Verify installation:
node -v
npm -v- Using NVM (Node Version Manager)
- Install NVM:
curl -fsSL https://raw.githubusercontent.com/nvm-sh/nvm/v0.39.7/install.sh | bash
source ~/.bashrc- Install Node.js (latest):
nvm install nodeOr a specific version:
nvm install 18.16.0- Verify installation:
node -v
npm -vLearn more here, and see our expert guide for Node.js–PostgreSQL setup on Ubuntu.
Test the Node.js Installation
Take the following simple steps to see if Node.js and NPM are installed and operating correctly on your system:
- Check Node.js and NPM Versions
Open a terminal and type these commands:
node -v
npm -vVersion numbers will appear on the screen if it is installed correctly; for example, v22.0.0 for Node.js and 10.0.0 for NPM (versions may vary).
- Run a Simple Program
Create a file called hello.js with the following content:
console.log('Node is installed!');Then run it in your terminal:
node hello.jsYou should see:
Node is installed!This shows that JavaScript files can be run from the command line using Node.js.
Check out our expert article to master Dockerizing a Node.js web app.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
In conclusion, Node.js provides a fast, scalable platform for modern web development. This article also covers the key steps to set up Node.js and NPM on Debian 12, helping you get started quickly and easily.
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to fix the “554 5.7.1 : Relay access denied” error.







0 Comments