Apache keeps going down on a Plesk server and causing trouble? We have your back.
At Bobcares, we offer solutions for every query, big and small, as a part of our Server Management Service.
Let’s take a look at how our Support Team recently helped out a customer when Apache keeps going down on a Plesk server.
What to do if Apache keeps going down on a Plesk server
Is your Apache webserver going down periodically while displaying the following error messages in the error log?
server reached MaxRequestWorkers setting, consider raising the MaxRequestWorkers setting
We can find the message in the following error logs:
- On Debian/Ubunty-based distributions:/var/log/apache2/error.log
- On CentOS/RHEL-based distributions: /var/log/httpd/error_log
According to our Support Techs, this specific error is due to MaxRequestWorkers reaching the limit with no more free workers for serving new requests to Apache. In other words, the requests are served slowly or in some cases, not served at all.
The solution to this error involves adjusting the MaxRequestWorkers settings for Apache. We can do this with the following command:
# MaxRequestWorkers = (Total RAM - Memory used for Linux, DB, etc.) / process size
MPM Event: Did you know the default ServerLimit is 16? We can increase it according to our requirements. However, we also need to raise MaxRequestWorkers with this formula: ServerLimit value x 25 = MaxRequestWorkers value.
For instance, if ServerLimit is value is 30, then MaxRequestWorkers will be 30 x 25 = 750.
MPM Prefork: The default value of MaxRequestWorkers is 256. If we raise, we also have to raise ServerLimit.
For CentOS/RHEL-based distribution
- First, we will find which MPM (Multi-Processing Module) is in use with the following command:
# httpd -V | grep MPM
- Next, we will open the /etc/httpd/conf.modules.d/01-cgi.conf file and modify the values of the following directives:
- For MPM Prefork:
LoadModule cgi_module modules/mod_cgi.so MaxRequestWorkers 400 ServerLimit 400
- For MPM Event:
LoadModule cgid_module modules/mod_cgid.so MaxRequestWorkers 400 ServerLimit 16
- For MPM Prefork:
- Finally restart Apache to apply the changes with this command:
# service httpd restart
For Debian/Ubuntu-based distribution
- First, we will find which MPM (Multi-Processing Module) is in use with the following command:
# apache2ctl -V | grep MPM
- Next, we will change the MPM configuration:
- For MPM Prefork:
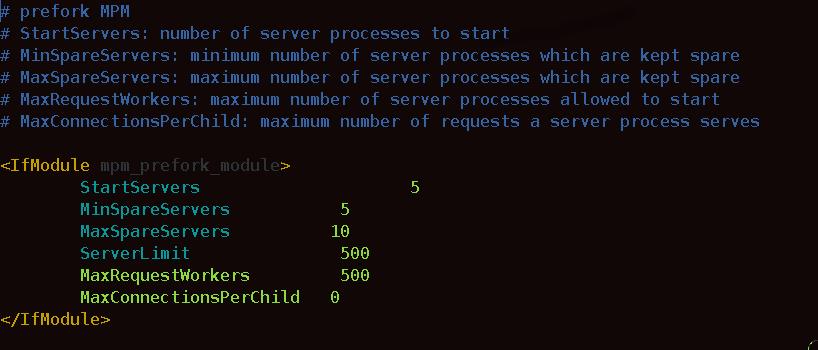
We have to open the /etc/apache2/mods-enabled/mpm_prefork.conf file and increase the values of these directives:
MaxRequestWorkers 500 ServerLimit 500
- For MPM Event:
We have to open the //etc/apache2/mods-enabled/mpm_event.conf file and increase the values of these directives:
MaxRequestWorkers 500 ServerLimit 16
- For MPM Prefork:
- Finally restart Apache to apply the changes with this command:
# service apache2 restart
[Looking for a solution to another query? We are just a click away.]
Conclusion
In short, the skilled Support Engineers at Bobcares demonstrated what to do when Apache keeps going down on a Plesk server.
PREVENT YOUR SERVER FROM CRASHING!
Never again lose customers to poor server speed! Let us help you.
Our server experts will monitor & maintain your server 24/7 so that it remains lightning fast and secure.








Thanks For this tutorial. Helps a lot