Learn more about setting up DMARC in cPanel for email security. Our cPanel Support team is here to help you with your questions and concerns.
Step-by-Step Guide to Setting DMARC in cPanel
DMARC, short for “Domain-based Message Authentication, Reporting, and Conformance,” is an email authentication protocol designed to protect our domain from email spoofing and phishing attacks. By doing so, it verifies the authenticity of emails sent from our domain, and as a result, DMARC helps safeguard our organization’s communication channels.
DMARC standardizes email authentication by combining two existing protocols:
- SPF (Sender Policy Framework):
This validates that emails come from authorized servers.
- DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail):
This ensures emails are not tampered with in transit.
With DMARC, only authenticated emails are trusted, helping to prevent malicious actors from pretending to impersonate our domain.
Key Components of a DMARC Record
A DMARC record contains essential tags that dictate how email authentication and reporting should function:
- Version Tag (v)
- Mandatory component
- Specifically, it is always set to `DMARC1`
- Specifies the DMARC protocol version in use
- Required for DMARC verification to be executed
- Policy Tag (p)
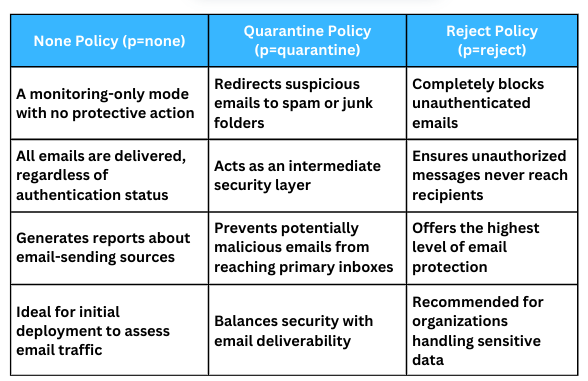
There are three possible policy options:
- None: Log entries but take no action
- Quarantine: Mark suspicious emails as spam
- Reject: Completely bounce unauthorized email messages
- Subdomain Policy Tag (sp)
It sets subdomain policy rules, which can differ from the main domain’s policy. Furthermore, it allows fine-tuned control over email authentication.
- Percentage Tag (pct)
This tag determines the percentage of emails subjected to the DMARC policy. It usually ranges from 0% to 100%. Importantly, it is useful for gradually enforcing DMARC rules.
- Aggregate Reports Tag (rua)
This tag specifies the email address to which aggregate reports will be received. In particular, these XML reports provide insights into email traffic and authentication results.
- Forensic Reports Tag (ruf)
This tag designates the email address for forensic reports. It sends detailed copies of failed authentication emails, helping troubleshoot issues and identify potential threats.
Sample DMARC Record
v=DMARC1; p=reject; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com; pct=100This record enforces strict email authentication, blocking unauthorized messages while gathering comprehensive reporting data.
DMARC Policy Options
DMARC offers three policy levels to manage email authentication outcomes:
Implementation Strategy
According to our Experts, a phased approach to DMARC implementation helps prevent disruptions:
- Start with None policy: Monitor email traffic without blocking emails.
- Progress to Quarantine: Gradually move suspicious emails to spam folders.
- Adopt Reject policy: Fully enforce email authentication once confident in the settings.
Additional DMARC Configuration Options
- Percentage Tag (pct):
Gradually enforce policies by adjusting the percentage of emails affected.
- Subdomain Policy (sp):
Customize policies for subdomains separate from the root domain.
- Alignment Modes:
Configure strictness for SPF and DKIM alignment checks.
Benefits of DMARC Implementation
- DMARC reduces unnecessary email blocking by verifying email authenticity, ensuring legitimate messages reach recipients without being mistakenly filtered.
- It tracks all email sources using your domain.
- Also, it helps uncover security vulnerabilities.
- Additionally, it blocks domain impersonation.
- It prevents exact-domain phishing attacks.
- DMARC mitigates Business Email Compromise (BEC) risks
- It increases deliverability rates.
- It offers a higher inbox placement and better engagement metrics.
- Also, it monitors all emails sent from our domain.
- Furthermore, it identifies both authorized and unauthorized sources.
Step-by-Step DMARC Setup in cPanel
- First, log into cPanel and make sure you have admin rights to manage DNS records.
- Then, go to the Domains section and select Zone Editor or Advanced DNS Zone Editor.
- Now, choose the domain for DMARC setup.
- Next, click Add Record or +Add Record and set the record type to TXT.
- Then, configure the following:
- Name: `_dmarc`
- TTL: 3600 (or default value)
- Value: DMARC record configuration
DMARC Record Configuration
Here is a sample record:
v=DMARC1; p=none; rua=mailto:dmarc-reports@yourdomain.com; ruf=mailto:dmarc-forensic@yourdomain.comHere is the breakdown:
- v=DMARC1: Protocol version
- p=none: Monitoring mode
- rua: Aggregate reporting email
- ruf: Forensic reporting email
Once we are done adding the record, allow 1-2 hours for DNS propagation. Meanwhile, we can use DMARC record checkers to confirm the configuration. Additionally, we can review initial reports to monitor email traffic.
Tips for Effective DMARC Implementation
- Ensure SPF and DKIM are configured before enabling DMARC.
- Also, begin with p=none to gather data without blocking emails.
- Gradually increase enforcement to quarantine and reject.
- Additionally, use dedicated email addresses to receive DMARC reports.
[Need assistance with a different issue? Our team is available 24/7.]
Conclusion
By implementing DMARC step-by-step, we can improve your email security, reduce phishing risks, and enhance deliverability.
In brief, our Support Experts demonstrated how to set up DMARC in cPanel for email security.







0 Comments